Introduction: Google Cloud Build provides a fully managed CI/CD platform that executes builds on Google’s infrastructure with automatic scaling and pay-per-use pricing. This comprehensive guide explores Cloud Build’s enterprise capabilities, from multi-stage pipelines and artifact management to security scanning, approval workflows, and deployment automation. After implementing CI/CD pipelines for organizations deploying hundreds of times daily, I’ve found Cloud Build delivers exceptional value through its native GCP integration, flexible build configurations, and robust security features. Organizations should leverage Cloud Build’s container-based execution, Artifact Registry integration, and Cloud Deploy for progressive delivery while implementing proper security controls and approval gates from the start.
Cloud Build Architecture: Serverless CI/CD
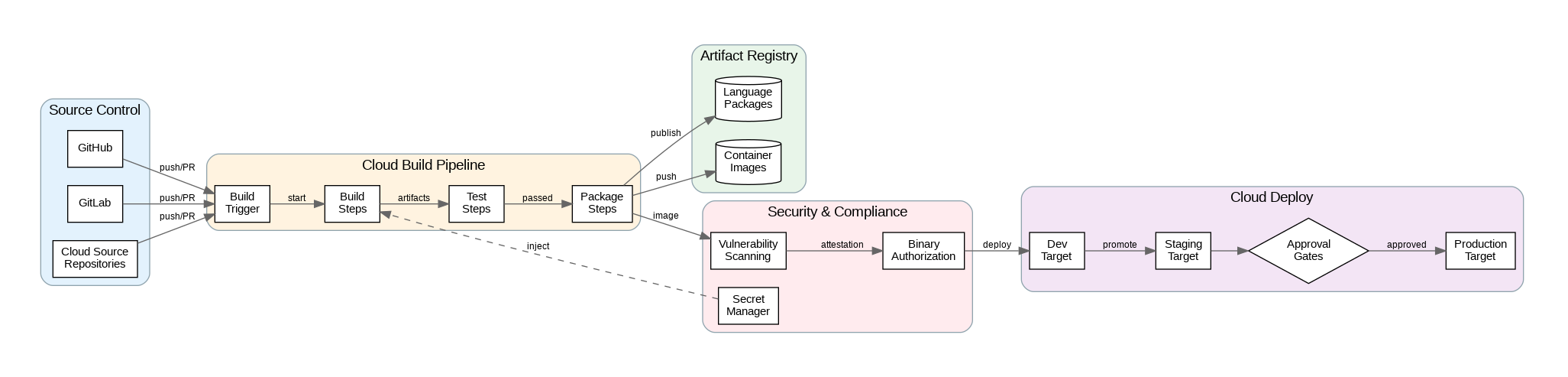
Cloud Build executes builds in isolated containers on Google’s infrastructure, eliminating the need to manage build servers. Each build step runs in a separate container, enabling language-agnostic pipelines that can use any Docker image. Build steps share a workspace volume, allowing artifacts to pass between steps. This container-based model provides reproducibility—builds produce identical results regardless of when or where they run.
Triggers automate build execution in response to events. Repository triggers fire on pushes, pull requests, or tag creation in Cloud Source Repositories, GitHub, GitLab, or Bitbucket. Pub/Sub triggers enable event-driven builds from any GCP service. Manual triggers with substitution variables support parameterized builds for different environments or configurations. Configure trigger filters to run specific builds based on branch patterns, file paths, or commit messages.
Build pools provide dedicated, persistent workers for builds requiring specific configurations or network access. Private pools run in your VPC, enabling builds that access private resources like internal registries or databases. Regional pools reduce latency by running builds close to your source repositories and deployment targets. For most workloads, the default shared pool provides sufficient performance at lower cost.
Pipeline Design and Security
Multi-stage pipelines separate concerns into logical phases: build, test, scan, and deploy. Use build step dependencies (waitFor) to parallelize independent steps while maintaining correct ordering for dependent steps. Cache frequently used dependencies using Cloud Storage buckets to reduce build times. For monorepos, implement path-based filtering to build only affected components.
Security scanning integrates throughout the pipeline. Container Analysis scans images for known vulnerabilities during builds. Binary Authorization enforces deployment policies, requiring images to pass vulnerability thresholds and be signed by trusted attestors before deployment. Secret Manager integration provides secure access to credentials without embedding them in build configurations or source code.
Approval workflows gate deployments to sensitive environments. Cloud Deploy provides managed delivery pipelines with approval gates, canary deployments, and automatic rollbacks. Configure approval requirements by environment—development deploys automatically, staging requires team lead approval, production requires multiple approvers. Audit logs track all approvals and deployments for compliance.
Production Terraform Configuration
Here’s a comprehensive Terraform configuration for Cloud Build with enterprise CI/CD patterns:
# Cloud Build Enterprise Configuration
terraform {
required_version = ">= 1.5.0"
required_providers {
google = { source = "hashicorp/google", version = "~> 5.0" }
}
}
variable "project_id" { type = string }
variable "region" { type = string, default = "us-central1" }
variable "github_owner" { type = string }
variable "github_repo" { type = string }
# Enable required APIs
resource "google_project_service" "apis" {
for_each = toset([
"cloudbuild.googleapis.com",
"artifactregistry.googleapis.com",
"containeranalysis.googleapis.com",
"binaryauthorization.googleapis.com",
"clouddeploy.googleapis.com",
"secretmanager.googleapis.com"
])
service = each.value
disable_on_destroy = false
}
# Artifact Registry for container images
resource "google_artifact_registry_repository" "containers" {
location = var.region
repository_id = "containers"
format = "DOCKER"
docker_config {
immutable_tags = true
}
cleanup_policies {
id = "keep-recent"
action = "KEEP"
most_recent_versions {
keep_count = 10
}
}
}
# Cloud Build service account
resource "google_service_account" "cloudbuild" {
account_id = "cloudbuild-sa"
display_name = "Cloud Build Service Account"
}
# IAM permissions for Cloud Build
resource "google_project_iam_member" "cloudbuild_permissions" {
for_each = toset([
"roles/cloudbuild.builds.builder",
"roles/artifactregistry.writer",
"roles/container.developer",
"roles/secretmanager.secretAccessor",
"roles/clouddeploy.releaser"
])
project = var.project_id
role = each.value
member = "serviceAccount:${google_service_account.cloudbuild.email}"
}
# Secret for GitHub token
resource "google_secret_manager_secret" "github_token" {
secret_id = "github-token"
replication {
auto {}
}
}
# GitHub connection
resource "google_cloudbuildv2_connection" "github" {
location = var.region
name = "github-connection"
github_config {
app_installation_id = 12345678 # Replace with actual installation ID
authorizer_credential {
oauth_token_secret_version = google_secret_manager_secret_version.github_token.id
}
}
}
resource "google_secret_manager_secret_version" "github_token" {
secret = google_secret_manager_secret.github_token.id
secret_data = "ghp_xxxxxxxxxxxx" # Replace with actual token
}
# GitHub repository connection
resource "google_cloudbuildv2_repository" "repo" {
location = var.region
name = var.github_repo
parent_connection = google_cloudbuildv2_connection.github.id
remote_uri = "https://github.com/${var.github_owner}/${var.github_repo}.git"
}
# Build trigger for main branch
resource "google_cloudbuild_trigger" "main_branch" {
name = "main-branch-build"
location = var.region
repository_event_config {
repository = google_cloudbuildv2_repository.repo.id
push {
branch = "^main$"
}
}
service_account = google_service_account.cloudbuild.id
build {
step {
name = "gcr.io/cloud-builders/docker"
args = [
"build",
"-t", "${var.region}-docker.pkg.dev/${var.project_id}/containers/app:$COMMIT_SHA",
"-t", "${var.region}-docker.pkg.dev/${var.project_id}/containers/app:latest",
"."
]
}
step {
name = "gcr.io/cloud-builders/docker"
args = ["push", "--all-tags", "${var.region}-docker.pkg.dev/${var.project_id}/containers/app"]
}
step {
name = "gcr.io/google.com/cloudsdktool/cloud-sdk"
entrypoint = "gcloud"
args = [
"deploy", "releases", "create", "release-$SHORT_SHA",
"--delivery-pipeline", "app-pipeline",
"--region", var.region,
"--images", "app=${var.region}-docker.pkg.dev/${var.project_id}/containers/app:$COMMIT_SHA"
]
}
options {
logging = "CLOUD_LOGGING_ONLY"
}
timeout = "1200s"
}
}
# Build trigger for pull requests
resource "google_cloudbuild_trigger" "pull_request" {
name = "pull-request-build"
location = var.region
repository_event_config {
repository = google_cloudbuildv2_repository.repo.id
pull_request {
branch = "^main$"
}
}
service_account = google_service_account.cloudbuild.id
build {
step {
name = "gcr.io/cloud-builders/docker"
args = ["build", "-t", "app:pr-$_PR_NUMBER", "."]
}
step {
name = "gcr.io/cloud-builders/docker"
entrypoint = "sh"
args = ["-c", "docker run app:pr-$_PR_NUMBER npm test"]
}
step {
name = "gcr.io/google.com/cloudsdktool/cloud-sdk"
entrypoint = "gcloud"
args = [
"artifacts", "docker", "images", "scan",
"app:pr-$_PR_NUMBER",
"--format=json"
]
}
timeout = "600s"
}
}
# Cloud Deploy delivery pipeline
resource "google_clouddeploy_delivery_pipeline" "app_pipeline" {
location = var.region
name = "app-pipeline"
serial_pipeline {
stages {
target_id = google_clouddeploy_target.dev.name
}
stages {
target_id = google_clouddeploy_target.staging.name
}
stages {
target_id = google_clouddeploy_target.prod.name
}
}
}
# Deployment targets
resource "google_clouddeploy_target" "dev" {
location = var.region
name = "dev"
gke {
cluster = "projects/${var.project_id}/locations/${var.region}/clusters/dev-cluster"
}
require_approval = false
}
resource "google_clouddeploy_target" "staging" {
location = var.region
name = "staging"
gke {
cluster = "projects/${var.project_id}/locations/${var.region}/clusters/staging-cluster"
}
require_approval = true
}
resource "google_clouddeploy_target" "prod" {
location = var.region
name = "prod"
gke {
cluster = "projects/${var.project_id}/locations/${var.region}/clusters/prod-cluster"
}
require_approval = true
execution_configs {
usages = ["RENDER", "DEPLOY"]
service_account = google_service_account.cloudbuild.email
}
}
# Binary Authorization policy
resource "google_binary_authorization_policy" "policy" {
admission_whitelist_patterns {
name_pattern = "gcr.io/google_containers/*"
}
default_admission_rule {
evaluation_mode = "REQUIRE_ATTESTATION"
enforcement_mode = "ENFORCED_BLOCK_AND_AUDIT_LOG"
require_attestations_by = [
google_binary_authorization_attestor.build_attestor.name
]
}
cluster_admission_rules {
cluster = "${var.region}.dev-cluster"
evaluation_mode = "ALWAYS_ALLOW"
enforcement_mode = "ENFORCED_BLOCK_AND_AUDIT_LOG"
}
}
resource "google_binary_authorization_attestor" "build_attestor" {
name = "build-attestor"
attestation_authority_note {
note_reference = google_container_analysis_note.build_note.name
}
}
resource "google_container_analysis_note" "build_note" {
name = "build-attestation"
attestation_authority {
hint {
human_readable_name = "Cloud Build Attestor"
}
}
}Python SDK for Build Automation
This Python implementation demonstrates enterprise patterns for Cloud Build including programmatic trigger management and build monitoring:
"""Cloud Build Manager - Enterprise Python Implementation"""
from dataclasses import dataclass
from typing import List, Dict, Optional
from google.cloud.devtools import cloudbuild_v1
from google.cloud import artifactregistry_v1
from google.protobuf import duration_pb2
import logging
from datetime import datetime, timedelta
logging.basicConfig(level=logging.INFO)
logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
@dataclass
class BuildStatus:
build_id: str
status: str
start_time: datetime
duration_seconds: int
images: List[str]
logs_url: str
@dataclass
class TriggerConfig:
name: str
branch_pattern: str
build_steps: List[Dict]
timeout_seconds: int = 600
class CloudBuildManager:
"""Enterprise Cloud Build management."""
def __init__(self, project_id: str, region: str = "global"):
self.project_id = project_id
self.region = region
self.client = cloudbuild_v1.CloudBuildClient()
self.parent = f"projects/{project_id}/locations/{region}"
def create_trigger(self, config: TriggerConfig,
repo_name: str) -> str:
"""Create build trigger."""
steps = [
cloudbuild_v1.BuildStep(
name=step["name"],
args=step.get("args", []),
entrypoint=step.get("entrypoint"),
env=step.get("env", [])
)
for step in config.build_steps
]
trigger = cloudbuild_v1.BuildTrigger(
name=config.name,
github=cloudbuild_v1.GitHubEventsConfig(
owner="your-org",
name=repo_name,
push=cloudbuild_v1.PushFilter(
branch=config.branch_pattern
)
),
build=cloudbuild_v1.Build(
steps=steps,
timeout=duration_pb2.Duration(seconds=config.timeout_seconds)
)
)
result = self.client.create_build_trigger(
parent=self.parent,
trigger=trigger
)
logger.info(f"Created trigger: {result.name}")
return result.id
def run_trigger(self, trigger_id: str,
branch: str = "main",
substitutions: Dict[str, str] = None) -> str:
"""Manually run a build trigger."""
source = cloudbuild_v1.RepoSource(
branch_name=branch,
substitutions=substitutions or {}
)
operation = self.client.run_build_trigger(
name=f"{self.parent}/triggers/{trigger_id}",
source=source
)
build = operation.result()
logger.info(f"Started build: {build.id}")
return build.id
def get_build_status(self, build_id: str) -> BuildStatus:
"""Get build status and details."""
build = self.client.get_build(
name=f"{self.parent}/builds/{build_id}"
)
duration = 0
if build.finish_time and build.start_time:
duration = int((build.finish_time - build.start_time).total_seconds())
return BuildStatus(
build_id=build.id,
status=cloudbuild_v1.Build.Status(build.status).name,
start_time=build.start_time,
duration_seconds=duration,
images=list(build.images),
logs_url=build.log_url
)
def wait_for_build(self, build_id: str,
timeout_minutes: int = 30) -> BuildStatus:
"""Wait for build to complete."""
import time
deadline = datetime.utcnow() + timedelta(minutes=timeout_minutes)
while datetime.utcnow() < deadline:
status = self.get_build_status(build_id)
if status.status in ["SUCCESS", "FAILURE", "CANCELLED", "TIMEOUT"]:
return status
logger.info(f"Build {build_id} status: {status.status}")
time.sleep(10)
raise TimeoutError(f"Build {build_id} did not complete within {timeout_minutes} minutes")
def list_recent_builds(self, limit: int = 10) -> List[BuildStatus]:
"""List recent builds."""
request = cloudbuild_v1.ListBuildsRequest(
parent=self.parent,
page_size=limit
)
builds = []
for build in self.client.list_builds(request=request):
duration = 0
if build.finish_time and build.start_time:
duration = int((build.finish_time - build.start_time).total_seconds())
builds.append(BuildStatus(
build_id=build.id,
status=cloudbuild_v1.Build.Status(build.status).name,
start_time=build.start_time,
duration_seconds=duration,
images=list(build.images),
logs_url=build.log_url
))
return builds
def cancel_build(self, build_id: str) -> bool:
"""Cancel a running build."""
try:
self.client.cancel_build(
name=f"{self.parent}/builds/{build_id}"
)
logger.info(f"Cancelled build: {build_id}")
return True
except Exception as e:
logger.error(f"Failed to cancel build: {e}")
return False
def get_build_metrics(self, days: int = 7) -> Dict:
"""Get build metrics for analysis."""
builds = []
request = cloudbuild_v1.ListBuildsRequest(
parent=self.parent,
page_size=1000
)
cutoff = datetime.utcnow() - timedelta(days=days)
for build in self.client.list_builds(request=request):
if build.start_time and build.start_time.replace(tzinfo=None) > cutoff:
builds.append(build)
if not builds:
return {"total": 0}
success = sum(1 for b in builds if b.status == cloudbuild_v1.Build.Status.SUCCESS)
failure = sum(1 for b in builds if b.status == cloudbuild_v1.Build.Status.FAILURE)
durations = [
(b.finish_time - b.start_time).total_seconds()
for b in builds
if b.finish_time and b.start_time
]
return {
"total": len(builds),
"success": success,
"failure": failure,
"success_rate": success / len(builds) * 100 if builds else 0,
"avg_duration_seconds": sum(durations) / len(durations) if durations else 0,
"max_duration_seconds": max(durations) if durations else 0
}Cost Optimization and Best Practices
Cloud Build pricing includes build minutes on different machine types. The default e2-medium provides sufficient resources for most builds at the lowest cost. Use larger machine types (e2-highcpu, n1-highcpu) only for builds that benefit from additional CPU or memory. Monitor build times and optimize slow steps—caching dependencies often provides the best cost/performance improvement.
Artifact Registry pricing includes storage and egress. Enable cleanup policies to automatically delete old images, keeping only recent versions. Use immutable tags for production images to prevent accidental overwrites. Configure vulnerability scanning to run automatically on push, catching security issues before deployment.
Build optimization strategies include parallelizing independent steps, caching dependencies in Cloud Storage, and using multi-stage Docker builds to reduce image sizes. For monorepos, implement path-based triggers to build only affected components. Consider using Kaniko for rootless container builds in environments with strict security requirements.
Key Takeaways and Best Practices
Cloud Build provides a powerful, serverless CI/CD platform with native GCP integration. Design pipelines with clear separation between build, test, scan, and deploy phases. Implement security scanning and Binary Authorization to enforce deployment policies. Use Cloud Deploy for managed progressive delivery with approval gates and automatic rollbacks.
Cache dependencies aggressively to reduce build times and costs. Monitor build metrics to identify optimization opportunities. The Terraform and Python examples provided here establish patterns for production-ready CI/CD pipelines that scale from small teams to enterprise deployments while maintaining security and compliance requirements.
Discover more from C4: Container, Code, Cloud & Context
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.