Introduction: Google Cloud Load Balancing and Cloud CDN provide enterprise-grade traffic distribution and content delivery for global applications. This comprehensive guide explores load balancing architectures, from HTTP(S) load balancers and TCP/UDP proxies to internal load balancing and traffic management policies. After implementing global load balancing for applications serving billions of requests daily, I’ve found Google’s load balancing delivers exceptional value through its anycast architecture, automatic scaling, and deep integration with Cloud CDN. Organizations should leverage these services for high-availability deployments, global traffic distribution, and edge caching while implementing proper health checks, SSL policies, and cost optimization from the start.
Load Balancing Architecture: Global and Regional Options
Google Cloud offers multiple load balancer types optimized for different use cases. External HTTP(S) Load Balancing provides global load balancing with anycast IP addresses, routing traffic to the nearest healthy backend. This architecture eliminates DNS-based failover delays and provides sub-second failover between regions. The load balancer terminates SSL at Google’s edge, reducing latency and offloading cryptographic processing from backends.
Regional load balancers serve traffic within a single region, offering lower latency for region-specific workloads. Internal load balancers distribute traffic between services within a VPC, enabling microservices architectures without exposing internal services to the internet. Choose internal load balancing for service-to-service communication and external load balancing for user-facing traffic.
Network load balancing operates at Layer 4, preserving client IP addresses and supporting any TCP/UDP protocol. Use network load balancing for non-HTTP workloads like gaming servers, VoIP, or custom protocols. For HTTP workloads, prefer HTTP(S) load balancing for its advanced features including URL-based routing, header manipulation, and Cloud CDN integration.
Cloud CDN: Edge Caching and Content Delivery
Cloud CDN caches content at Google’s edge locations worldwide, reducing latency and backend load. The CDN integrates directly with HTTP(S) Load Balancing—enable it with a single configuration change. Cache keys determine how content is cached and served; configure them based on URL path, query parameters, headers, or cookies to optimize cache hit rates.
Cache modes control caching behavior: USE_ORIGIN_HEADERS respects Cache-Control headers from backends, FORCE_CACHE_ALL caches all responses regardless of headers, and CACHE_ALL_STATIC caches common static file types. For dynamic content, use signed URLs or signed cookies to enable CDN caching while maintaining access control.
Cache invalidation removes stale content from edge caches. Invalidate by URL path or cache tag for granular control. However, invalidation has rate limits and propagation delays—design applications to use cache-busting URLs (versioned filenames) for frequently updated content rather than relying on invalidation.
Production Terraform Configuration
Here’s a comprehensive Terraform configuration for global load balancing with Cloud CDN:
# Cloud Load Balancing and CDN Enterprise Configuration
terraform {
required_version = ">= 1.5.0"
required_providers {
google = { source = "hashicorp/google", version = "~> 5.0" }
}
}
variable "project_id" { type = string }
variable "domain" { type = string }
# Enable required APIs
resource "google_project_service" "apis" {
for_each = toset([
"compute.googleapis.com",
"certificatemanager.googleapis.com"
])
service = each.value
disable_on_destroy = false
}
# Reserve global static IP
resource "google_compute_global_address" "default" {
name = "global-lb-ip"
}
# Managed SSL Certificate
resource "google_compute_managed_ssl_certificate" "default" {
name = "managed-cert"
managed {
domains = [var.domain, "www.${var.domain}"]
}
}
# Health check for backends
resource "google_compute_health_check" "http" {
name = "http-health-check"
check_interval_sec = 10
timeout_sec = 5
healthy_threshold = 2
unhealthy_threshold = 3
http_health_check {
port = 80
request_path = "/health"
}
}
# Instance template for backend VMs
resource "google_compute_instance_template" "web" {
name_prefix = "web-template-"
machine_type = "e2-medium"
disk {
source_image = "debian-cloud/debian-11"
auto_delete = true
boot = true
disk_size_gb = 20
}
network_interface {
network = "default"
access_config {}
}
metadata_startup_script = <<-EOF
#!/bin/bash
apt-get update
apt-get install -y nginx
echo "Server: $(hostname)" > /var/www/html/index.html
systemctl start nginx
EOF
tags = ["http-server", "https-server"]
lifecycle {
create_before_destroy = true
}
}
# Managed Instance Group - US
resource "google_compute_region_instance_group_manager" "us" {
name = "web-mig-us"
base_instance_name = "web-us"
region = "us-central1"
target_size = 2
version {
instance_template = google_compute_instance_template.web.id
}
named_port {
name = "http"
port = 80
}
auto_healing_policies {
health_check = google_compute_health_check.http.id
initial_delay_sec = 300
}
}
# Managed Instance Group - Europe
resource "google_compute_region_instance_group_manager" "eu" {
name = "web-mig-eu"
base_instance_name = "web-eu"
region = "europe-west1"
target_size = 2
version {
instance_template = google_compute_instance_template.web.id
}
named_port {
name = "http"
port = 80
}
auto_healing_policies {
health_check = google_compute_health_check.http.id
initial_delay_sec = 300
}
}
# Backend service with CDN enabled
resource "google_compute_backend_service" "default" {
name = "web-backend"
protocol = "HTTP"
port_name = "http"
timeout_sec = 30
health_checks = [google_compute_health_check.http.id]
load_balancing_scheme = "EXTERNAL_MANAGED"
# Enable Cloud CDN
enable_cdn = true
cdn_policy {
cache_mode = "CACHE_ALL_STATIC"
default_ttl = 3600
max_ttl = 86400
client_ttl = 3600
negative_caching = true
serve_while_stale = 86400
cache_key_policy {
include_host = true
include_protocol = true
include_query_string = false
}
}
# Connection draining
connection_draining_timeout_sec = 300
# Logging
log_config {
enable = true
sample_rate = 1.0
}
backend {
group = google_compute_region_instance_group_manager.us.instance_group
balancing_mode = "UTILIZATION"
capacity_scaler = 1.0
max_utilization = 0.8
}
backend {
group = google_compute_region_instance_group_manager.eu.instance_group
balancing_mode = "UTILIZATION"
capacity_scaler = 1.0
max_utilization = 0.8
}
}
# Backend bucket for static assets
resource "google_storage_bucket" "static" {
name = "${var.project_id}-static-assets"
location = "US"
uniform_bucket_level_access = true
cors {
origin = ["https://${var.domain}"]
method = ["GET", "HEAD"]
response_header = ["Content-Type", "Cache-Control"]
max_age_seconds = 3600
}
}
resource "google_compute_backend_bucket" "static" {
name = "static-backend"
bucket_name = google_storage_bucket.static.name
enable_cdn = true
cdn_policy {
cache_mode = "CACHE_ALL_STATIC"
default_ttl = 86400
max_ttl = 604800
serve_while_stale = 86400
}
}
# URL Map with path-based routing
resource "google_compute_url_map" "default" {
name = "web-url-map"
default_service = google_compute_backend_service.default.id
host_rule {
hosts = [var.domain, "www.${var.domain}"]
path_matcher = "main"
}
path_matcher {
name = "main"
default_service = google_compute_backend_service.default.id
path_rule {
paths = ["/static/*", "/assets/*", "/images/*"]
service = google_compute_backend_bucket.static.id
}
path_rule {
paths = ["/api/*"]
service = google_compute_backend_service.default.id
route_action {
retry_policy {
num_retries = 3
retry_conditions = ["5xx", "reset", "connect-failure"]
}
timeout {
seconds = 30
}
}
}
}
}
# HTTPS Target Proxy
resource "google_compute_target_https_proxy" "default" {
name = "https-proxy"
url_map = google_compute_url_map.default.id
ssl_certificates = [google_compute_managed_ssl_certificate.default.id]
ssl_policy = google_compute_ssl_policy.modern.id
}
# SSL Policy (modern ciphers only)
resource "google_compute_ssl_policy" "modern" {
name = "modern-ssl-policy"
profile = "MODERN"
min_tls_version = "TLS_1_2"
}
# Global Forwarding Rule
resource "google_compute_global_forwarding_rule" "https" {
name = "https-forwarding-rule"
ip_address = google_compute_global_address.default.address
port_range = "443"
target = google_compute_target_https_proxy.default.id
load_balancing_scheme = "EXTERNAL_MANAGED"
}
# HTTP to HTTPS redirect
resource "google_compute_url_map" "redirect" {
name = "http-redirect"
default_url_redirect {
https_redirect = true
strip_query = false
}
}
resource "google_compute_target_http_proxy" "redirect" {
name = "http-redirect-proxy"
url_map = google_compute_url_map.redirect.id
}
resource "google_compute_global_forwarding_rule" "http" {
name = "http-forwarding-rule"
ip_address = google_compute_global_address.default.address
port_range = "80"
target = google_compute_target_http_proxy.redirect.id
load_balancing_scheme = "EXTERNAL_MANAGED"
}
# Cloud Armor security policy
resource "google_compute_security_policy" "default" {
name = "web-security-policy"
rule {
action = "deny(403)"
priority = 1000
match {
expr {
expression = "origin.region_code == 'CN'"
}
}
description = "Block traffic from specific regions"
}
rule {
action = "throttle"
priority = 2000
match {
versioned_expr = "SRC_IPS_V1"
config {
src_ip_ranges = ["*"]
}
}
rate_limit_options {
conform_action = "allow"
exceed_action = "deny(429)"
rate_limit_threshold {
count = 100
interval_sec = 60
}
}
description = "Rate limiting"
}
rule {
action = "allow"
priority = 2147483647
match {
versioned_expr = "SRC_IPS_V1"
config {
src_ip_ranges = ["*"]
}
}
description = "Default allow"
}
}
# Outputs
output "load_balancer_ip" {
value = google_compute_global_address.default.address
}
output "cdn_enabled_backends" {
value = {
web_backend = google_compute_backend_service.default.enable_cdn
static_backend = google_compute_backend_bucket.static.enable_cdn
}
}Python SDK for Traffic Management
This Python implementation demonstrates load balancer management, CDN cache operations, and traffic analysis:
"""Cloud Load Balancing and CDN Management - Python SDK"""
from google.cloud import compute_v1
from google.api_core import retry
from datetime import datetime, timedelta
from typing import Optional, List, Dict, Any
import logging
logging.basicConfig(level=logging.INFO)
logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
class LoadBalancerManager:
"""Enterprise Load Balancer and CDN management."""
def __init__(self, project_id: str):
self.project_id = project_id
self.backend_services_client = compute_v1.BackendServicesClient()
self.url_maps_client = compute_v1.UrlMapsClient()
self.health_checks_client = compute_v1.HealthChecksClient()
self.ssl_certs_client = compute_v1.SslCertificatesClient()
self.addresses_client = compute_v1.GlobalAddressesClient()
# ==================== Backend Service Management ====================
def list_backend_services(self) -> List[Dict[str, Any]]:
"""List all backend services with health status."""
request = compute_v1.ListBackendServicesRequest(project=self.project_id)
backends = []
for backend in self.backend_services_client.list(request=request):
backends.append({
'name': backend.name,
'protocol': backend.protocol,
'cdn_enabled': backend.enable_cdn,
'timeout_sec': backend.timeout_sec,
'backends': [
{
'group': b.group,
'balancing_mode': b.balancing_mode,
'capacity_scaler': b.capacity_scaler
}
for b in backend.backends
]
})
return backends
def get_backend_health(self, backend_service: str) -> Dict[str, Any]:
"""Get health status of all backends in a service."""
request = compute_v1.GetBackendServiceRequest(
project=self.project_id,
backend_service=backend_service
)
service = self.backend_services_client.get(request=request)
health_status = []
for backend in service.backends:
health_request = compute_v1.GetHealthBackendServiceRequest(
project=self.project_id,
backend_service=backend_service,
resource_group_reference=compute_v1.ResourceGroupReference(
group=backend.group
)
)
try:
health = self.backend_services_client.get_health(request=health_request)
for status in health.health_status:
health_status.append({
'instance': status.instance,
'health_state': status.health_state,
'ip_address': status.ip_address
})
except Exception as e:
logger.warning(f"Could not get health for {backend.group}: {e}")
return {
'backend_service': backend_service,
'health_status': health_status,
'healthy_count': sum(1 for h in health_status if h['health_state'] == 'HEALTHY'),
'total_count': len(health_status)
}
def update_backend_capacity(
self,
backend_service: str,
backend_group: str,
capacity_scaler: float
) -> None:
"""Update capacity scaler for traffic shifting."""
request = compute_v1.GetBackendServiceRequest(
project=self.project_id,
backend_service=backend_service
)
service = self.backend_services_client.get(request=request)
for backend in service.backends:
if backend_group in backend.group:
backend.capacity_scaler = capacity_scaler
break
update_request = compute_v1.UpdateBackendServiceRequest(
project=self.project_id,
backend_service=backend_service,
backend_service_resource=service
)
operation = self.backend_services_client.update(request=update_request)
logger.info(f"Updated capacity for {backend_group} to {capacity_scaler}")
# ==================== CDN Cache Management ====================
def invalidate_cache(
self,
url_map: str,
path: str,
host: Optional[str] = None
) -> str:
"""Invalidate CDN cache for a specific path."""
cache_invalidation = compute_v1.CacheInvalidationRule(
path=path,
host=host
)
request = compute_v1.InvalidateCacheUrlMapRequest(
project=self.project_id,
url_map=url_map,
cache_invalidation_rule=cache_invalidation
)
operation = self.url_maps_client.invalidate_cache(request=request)
logger.info(f"Cache invalidation initiated for path: {path}")
return operation.name
def update_cdn_policy(
self,
backend_service: str,
cache_mode: str = "CACHE_ALL_STATIC",
default_ttl: int = 3600,
max_ttl: int = 86400
) -> None:
"""Update CDN caching policy for a backend service."""
request = compute_v1.GetBackendServiceRequest(
project=self.project_id,
backend_service=backend_service
)
service = self.backend_services_client.get(request=request)
if not service.cdn_policy:
service.cdn_policy = compute_v1.BackendServiceCdnPolicy()
service.cdn_policy.cache_mode = cache_mode
service.cdn_policy.default_ttl = default_ttl
service.cdn_policy.max_ttl = max_ttl
update_request = compute_v1.UpdateBackendServiceRequest(
project=self.project_id,
backend_service=backend_service,
backend_service_resource=service
)
self.backend_services_client.update(request=update_request)
logger.info(f"Updated CDN policy for {backend_service}")
# ==================== URL Map Management ====================
def get_url_map_config(self, url_map: str) -> Dict[str, Any]:
"""Get URL map routing configuration."""
request = compute_v1.GetUrlMapRequest(
project=self.project_id,
url_map=url_map
)
url_map_obj = self.url_maps_client.get(request=request)
config = {
'name': url_map_obj.name,
'default_service': url_map_obj.default_service,
'host_rules': [],
'path_matchers': []
}
for host_rule in url_map_obj.host_rules:
config['host_rules'].append({
'hosts': list(host_rule.hosts),
'path_matcher': host_rule.path_matcher
})
for matcher in url_map_obj.path_matchers:
path_rules = []
for rule in matcher.path_rules:
path_rules.append({
'paths': list(rule.paths),
'service': rule.service
})
config['path_matchers'].append({
'name': matcher.name,
'default_service': matcher.default_service,
'path_rules': path_rules
})
return config
def add_path_rule(
self,
url_map: str,
path_matcher: str,
paths: List[str],
backend_service: str
) -> None:
"""Add a new path rule to URL map."""
request = compute_v1.GetUrlMapRequest(
project=self.project_id,
url_map=url_map
)
url_map_obj = self.url_maps_client.get(request=request)
for matcher in url_map_obj.path_matchers:
if matcher.name == path_matcher:
new_rule = compute_v1.PathRule(
paths=paths,
service=backend_service
)
matcher.path_rules.append(new_rule)
break
update_request = compute_v1.UpdateUrlMapRequest(
project=self.project_id,
url_map=url_map,
url_map_resource=url_map_obj
)
self.url_maps_client.update(request=update_request)
logger.info(f"Added path rule for {paths} to {url_map}")
# ==================== SSL Certificate Management ====================
def list_ssl_certificates(self) -> List[Dict[str, Any]]:
"""List all SSL certificates with expiration info."""
request = compute_v1.ListSslCertificatesRequest(project=self.project_id)
certs = []
for cert in self.ssl_certs_client.list(request=request):
cert_info = {
'name': cert.name,
'type': cert.type_,
'creation_timestamp': cert.creation_timestamp
}
if cert.managed:
cert_info['domains'] = list(cert.managed.domains)
cert_info['status'] = cert.managed.status
if cert.expire_time:
cert_info['expire_time'] = cert.expire_time
certs.append(cert_info)
return certs
# ==================== Traffic Analysis ====================
def analyze_traffic_distribution(
self,
backend_service: str
) -> Dict[str, Any]:
"""Analyze traffic distribution across backends."""
health = self.get_backend_health(backend_service)
request = compute_v1.GetBackendServiceRequest(
project=self.project_id,
backend_service=backend_service
)
service = self.backend_services_client.get(request=request)
distribution = []
total_capacity = sum(b.capacity_scaler for b in service.backends)
for backend in service.backends:
region = backend.group.split('/')[8] if '/regions/' in backend.group else 'global'
distribution.append({
'group': backend.group.split('/')[-1],
'region': region,
'capacity_scaler': backend.capacity_scaler,
'traffic_percentage': (backend.capacity_scaler / total_capacity * 100) if total_capacity > 0 else 0,
'balancing_mode': backend.balancing_mode,
'max_utilization': backend.max_utilization
})
return {
'backend_service': backend_service,
'distribution': distribution,
'health_summary': {
'healthy': health['healthy_count'],
'total': health['total_count']
}
}
# Example usage
if __name__ == "__main__":
manager = LoadBalancerManager(project_id="my-project")
# List backend services
backends = manager.list_backend_services()
for backend in backends:
print(f"Backend: {backend['name']}, CDN: {backend['cdn_enabled']}")
# Check backend health
health = manager.get_backend_health("web-backend")
print(f"Healthy backends: {health['healthy_count']}/{health['total_count']}")
# Invalidate CDN cache
manager.invalidate_cache(
url_map="web-url-map",
path="/static/*"
)
# Analyze traffic distribution
distribution = manager.analyze_traffic_distribution("web-backend")
for d in distribution['distribution']:
print(f"Region: {d['region']}, Traffic: {d['traffic_percentage']:.1f}%")Cost Optimization and Performance Tuning
Load balancing costs include forwarding rules, backend services, and data processing. Optimize by consolidating multiple services behind a single load balancer using URL-based routing. Use regional load balancers for region-specific workloads to avoid global load balancing premiums. Monitor data processing costs and optimize backend responses to reduce egress.
Cloud CDN significantly reduces costs by serving cached content from edge locations. Monitor cache hit ratios through Cloud Monitoring—aim for 80%+ hit rates for static content. Configure appropriate TTLs based on content freshness requirements. Use cache tags for efficient invalidation of related content without invalidating entire paths.
Performance tuning involves optimizing health check intervals, connection draining timeouts, and backend capacity settings. Configure health checks to detect failures quickly without causing false positives—10-second intervals with 2 healthy/3 unhealthy thresholds work well for most applications. Enable connection draining to gracefully handle backend removals during deployments.
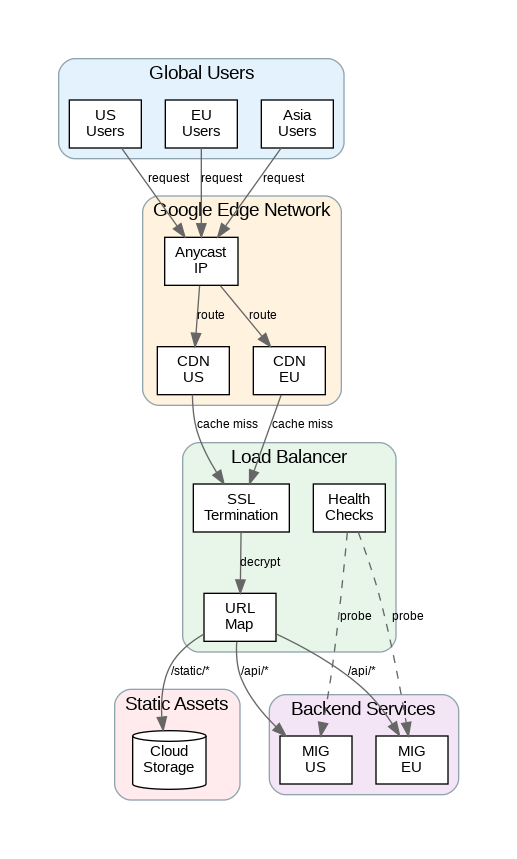
Key Takeaways and Best Practices
Google Cloud Load Balancing provides enterprise-grade traffic distribution with global anycast architecture and sub-second failover. Choose the appropriate load balancer type based on protocol requirements and traffic patterns. Enable Cloud CDN for static content to reduce latency and backend load while optimizing cache policies for your content types.
Implement comprehensive health checks and monitoring to ensure high availability. The Terraform and Python examples provided here establish patterns for production-ready global load balancing that scales from single-region deployments to worldwide traffic distribution while maintaining security through Cloud Armor integration and SSL policy enforcement.
Discover more from C4: Container, Code, Cloud & Context
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.