Introduction: Hugging Face Transformers has become the de facto standard library for working with transformer-based models. With access to over 500,000 pre-trained models and 150,000 datasets through the Hugging Face Hub, it provides the most comprehensive ecosystem for deploying open-source AI models. Whether you’re running Llama, Mistral, or fine-tuning your own models, Transformers offers a unified API that works across PyTorch, TensorFlow, and JAX. This guide covers everything from quick inference with pipelines to production deployment with Text Generation Inference.
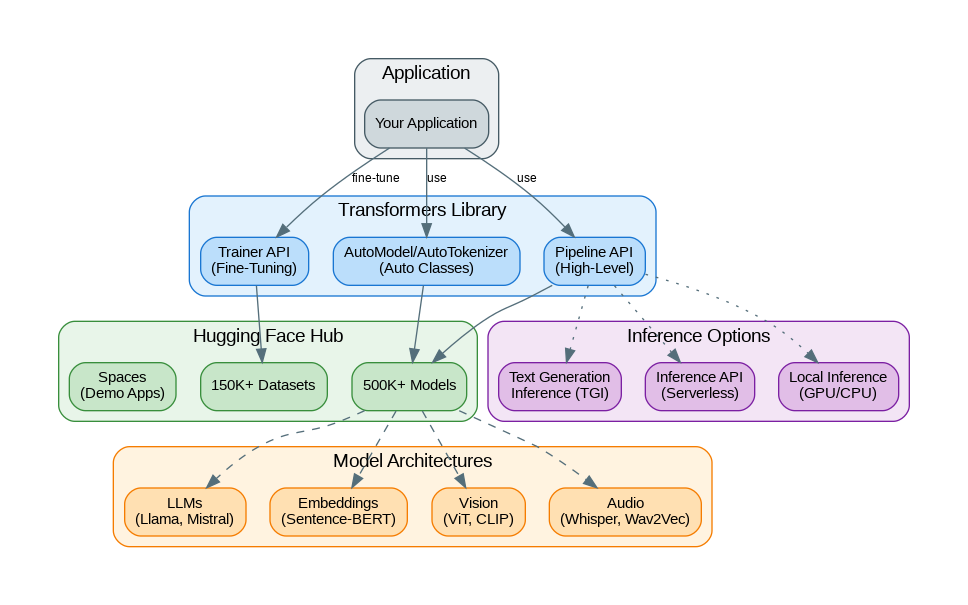
Capabilities and Features
Hugging Face Transformers provides comprehensive capabilities for working with AI models:
- 500K+ Models: Access to the largest collection of pre-trained models
- Pipeline API: High-level interface for common tasks (text generation, classification, etc.)
- AutoClasses: Automatic model and tokenizer loading with architecture detection
- Trainer API: Simplified fine-tuning with built-in optimization and evaluation
- Multi-Framework: Support for PyTorch, TensorFlow, and JAX
- Quantization: 4-bit and 8-bit quantization for efficient inference
- PEFT: Parameter-efficient fine-tuning (LoRA, QLoRA, etc.)
- Text Generation Inference: Production-ready inference server
- Inference API: Serverless inference for any Hub model
- Spaces: Deploy demo applications with Gradio or Streamlit
Getting Started
Install Transformers and set up your environment:
# Install core package
pip install transformers
# Install with PyTorch (recommended)
pip install transformers[torch]
# Install additional dependencies
pip install accelerate bitsandbytes sentencepiece
# For fine-tuning
pip install datasets peft trl
# Login to Hugging Face Hub (for gated models)
huggingface-cli loginQuick Start with Pipelines
The Pipeline API provides the fastest way to use models:
from transformers import pipeline
# Text Generation
generator = pipeline("text-generation", model="meta-llama/Llama-3.2-3B-Instruct")
response = generator(
"Explain quantum computing in simple terms:",
max_new_tokens=200,
temperature=0.7
)
print(response[0]["generated_text"])
# Text Classification
classifier = pipeline("sentiment-analysis")
result = classifier("I love using Hugging Face models!")
print(result) # [{'label': 'POSITIVE', 'score': 0.9998}]
# Question Answering
qa = pipeline("question-answering")
result = qa(
question="What is the capital of France?",
context="France is a country in Europe. Paris is its capital city."
)
print(result) # {'answer': 'Paris', 'score': 0.99}
# Embeddings
embedder = pipeline("feature-extraction", model="sentence-transformers/all-MiniLM-L6-v2")
embeddings = embedder("This is a sample sentence")
print(f"Embedding shape: {len(embeddings[0][0])}")
# Image Classification
image_classifier = pipeline("image-classification", model="google/vit-base-patch16-224")
result = image_classifier("path/to/image.jpg")
print(result)
# Speech Recognition
transcriber = pipeline("automatic-speech-recognition", model="openai/whisper-large-v3")
result = transcriber("path/to/audio.mp3")
print(result["text"])Working with LLMs
Load and use large language models with full control:
from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer
import torch
# Load model and tokenizer
model_name = "mistralai/Mistral-7B-Instruct-v0.3"
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_name)
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(
model_name,
torch_dtype=torch.bfloat16,
device_map="auto" # Automatically distribute across GPUs
)
# Chat format
messages = [
{"role": "system", "content": "You are a helpful AI assistant."},
{"role": "user", "content": "Write a Python function to calculate fibonacci numbers"}
]
# Apply chat template
input_text = tokenizer.apply_chat_template(
messages,
tokenize=False,
add_generation_prompt=True
)
# Tokenize and generate
inputs = tokenizer(input_text, return_tensors="pt").to(model.device)
outputs = model.generate(
**inputs,
max_new_tokens=500,
temperature=0.7,
top_p=0.9,
do_sample=True,
pad_token_id=tokenizer.eos_token_id
)
response = tokenizer.decode(outputs[0], skip_special_tokens=True)
print(response)
# Streaming generation
from transformers import TextStreamer
streamer = TextStreamer(tokenizer, skip_special_tokens=True)
outputs = model.generate(
**inputs,
max_new_tokens=500,
streamer=streamer
)Quantization for Efficient Inference
Run large models on consumer hardware with quantization:
from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer, BitsAndBytesConfig
import torch
# 4-bit quantization config
quantization_config = BitsAndBytesConfig(
load_in_4bit=True,
bnb_4bit_compute_dtype=torch.bfloat16,
bnb_4bit_quant_type="nf4",
bnb_4bit_use_double_quant=True
)
# Load quantized model
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(
"meta-llama/Llama-3.1-70B-Instruct",
quantization_config=quantization_config,
device_map="auto"
)
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("meta-llama/Llama-3.1-70B-Instruct")
# 70B model now fits on a single 24GB GPU!
print(f"Model memory: {model.get_memory_footprint() / 1e9:.2f} GB")
# 8-bit quantization (faster, slightly larger)
model_8bit = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(
"mistralai/Mistral-7B-Instruct-v0.3",
load_in_8bit=True,
device_map="auto"
)Fine-Tuning with PEFT and LoRA
Efficiently fine-tune models with parameter-efficient methods:
from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer, TrainingArguments
from peft import LoraConfig, get_peft_model, prepare_model_for_kbit_training
from trl import SFTTrainer
from datasets import load_dataset
# Load base model with quantization
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(
"meta-llama/Llama-3.2-3B-Instruct",
load_in_4bit=True,
device_map="auto"
)
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("meta-llama/Llama-3.2-3B-Instruct")
tokenizer.pad_token = tokenizer.eos_token
# Prepare model for training
model = prepare_model_for_kbit_training(model)
# Configure LoRA
lora_config = LoraConfig(
r=16, # Rank
lora_alpha=32,
target_modules=["q_proj", "k_proj", "v_proj", "o_proj"],
lora_dropout=0.05,
bias="none",
task_type="CAUSAL_LM"
)
model = get_peft_model(model, lora_config)
model.print_trainable_parameters() # ~0.5% of total parameters
# Load dataset
dataset = load_dataset("your-dataset", split="train")
# Training arguments
training_args = TrainingArguments(
output_dir="./lora-model",
num_train_epochs=3,
per_device_train_batch_size=4,
gradient_accumulation_steps=4,
learning_rate=2e-4,
warmup_steps=100,
logging_steps=10,
save_steps=500,
fp16=True
)
# Train with SFTTrainer
trainer = SFTTrainer(
model=model,
train_dataset=dataset,
args=training_args,
tokenizer=tokenizer,
max_seq_length=2048,
dataset_text_field="text"
)
trainer.train()
# Save and push to Hub
model.save_pretrained("./lora-model")
model.push_to_hub("your-username/your-model-lora")Text Generation Inference (TGI)
Deploy models in production with TGI:
# Run TGI server with Docker
docker run --gpus all --shm-size 1g -p 8080:80 \
-v $PWD/data:/data \
ghcr.io/huggingface/text-generation-inference:latest \
--model-id mistralai/Mistral-7B-Instruct-v0.3 \
--quantize bitsandbytes-nf4 \
--max-input-length 4096 \
--max-total-tokens 8192
# Python client
from huggingface_hub import InferenceClient
client = InferenceClient("http://localhost:8080")
# Generate text
response = client.text_generation(
"Explain machine learning:",
max_new_tokens=200,
temperature=0.7
)
print(response)
# Chat completion
response = client.chat_completion(
messages=[
{"role": "user", "content": "What is deep learning?"}
],
max_tokens=200
)
print(response.choices[0].message.content)
# Streaming
for token in client.text_generation(
"Write a story about AI:",
max_new_tokens=500,
stream=True
):
print(token, end="", flush=True)Inference API (Serverless)
from huggingface_hub import InferenceClient
import os
# Use Inference API for any Hub model
client = InferenceClient(token=os.environ["HF_TOKEN"])
# Text generation
response = client.text_generation(
"The future of AI is",
model="meta-llama/Llama-3.2-3B-Instruct",
max_new_tokens=100
)
print(response)
# Embeddings
embeddings = client.feature_extraction(
"This is a sample sentence",
model="sentence-transformers/all-MiniLM-L6-v2"
)
print(f"Embedding dimension: {len(embeddings[0])}")
# Image generation
image = client.text_to_image(
"A futuristic city with flying cars",
model="stabilityai/stable-diffusion-xl-base-1.0"
)
image.save("generated_image.png")Benchmarks and Performance
Hugging Face Transformers performance characteristics:
| Model | VRAM (4-bit) | Tokens/sec (A100) | Tokens/sec (RTX 4090) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Llama 3.2 3B | ~3GB | ~120 tok/s | ~80 tok/s |
| Mistral 7B | ~5GB | ~80 tok/s | ~50 tok/s |
| Llama 3.1 70B | ~40GB | ~25 tok/s | N/A (multi-GPU) |
| TGI (Mistral 7B) | ~5GB | ~150 tok/s | ~90 tok/s |
| Whisper Large v3 | ~4GB | ~30x realtime | ~20x realtime |
When to Use Hugging Face Transformers
Best suited for:
- Running open-source models locally or on your infrastructure
- Fine-tuning models on custom datasets
- Research and experimentation with latest architectures
- Building applications without API costs
- Privacy-sensitive applications requiring on-premise deployment
- Multi-modal applications (text, vision, audio)
Consider alternatives when:
- Need state-of-the-art performance (use GPT-4o or Claude)
- Don’t have GPU infrastructure (use API providers)
- Require managed infrastructure (use AWS Bedrock or Azure OpenAI)
- Building complex agent workflows (use LangChain/LangGraph)
References and Documentation
- Official Documentation: https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers
- Model Hub: https://huggingface.co/models
- GitHub Repository: https://github.com/huggingface/transformers
- TGI Documentation: https://huggingface.co/docs/text-generation-inference
- PEFT Documentation: https://huggingface.co/docs/peft
Conclusion
Hugging Face Transformers has democratized access to state-of-the-art AI models. The combination of an extensive model hub, intuitive APIs, and production-ready deployment options makes it possible to build sophisticated AI applications without relying on proprietary APIs. While closed-source models like GPT-4 and Claude still lead in raw capability, the gap is narrowing rapidly with models like Llama 3 and Mistral. For teams prioritizing cost control, privacy, or customization through fine-tuning, Hugging Face Transformers provides the most comprehensive and well-supported ecosystem available.
Discover more from C4: Container, Code, Cloud & Context
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.