Vertex AI represents Google Cloud’s unified machine learning platform, bringing together AutoML, custom training, model deployment, and MLOps capabilities under a single, cohesive experience. This comprehensive guide explores Vertex AI’s enterprise capabilities, from managed training pipelines and feature stores to model monitoring and A/B testing.
After building production ML systems across multiple cloud platforms, I’ve found Vertex AI delivers the most integrated and developer-friendly MLOps experience available. Organizations should leverage Vertex AI for end-to-end ML workflows, from experimentation to production deployment, while implementing proper model governance and cost controls from the start.
Vertex AI Architecture: Unified ML Platform
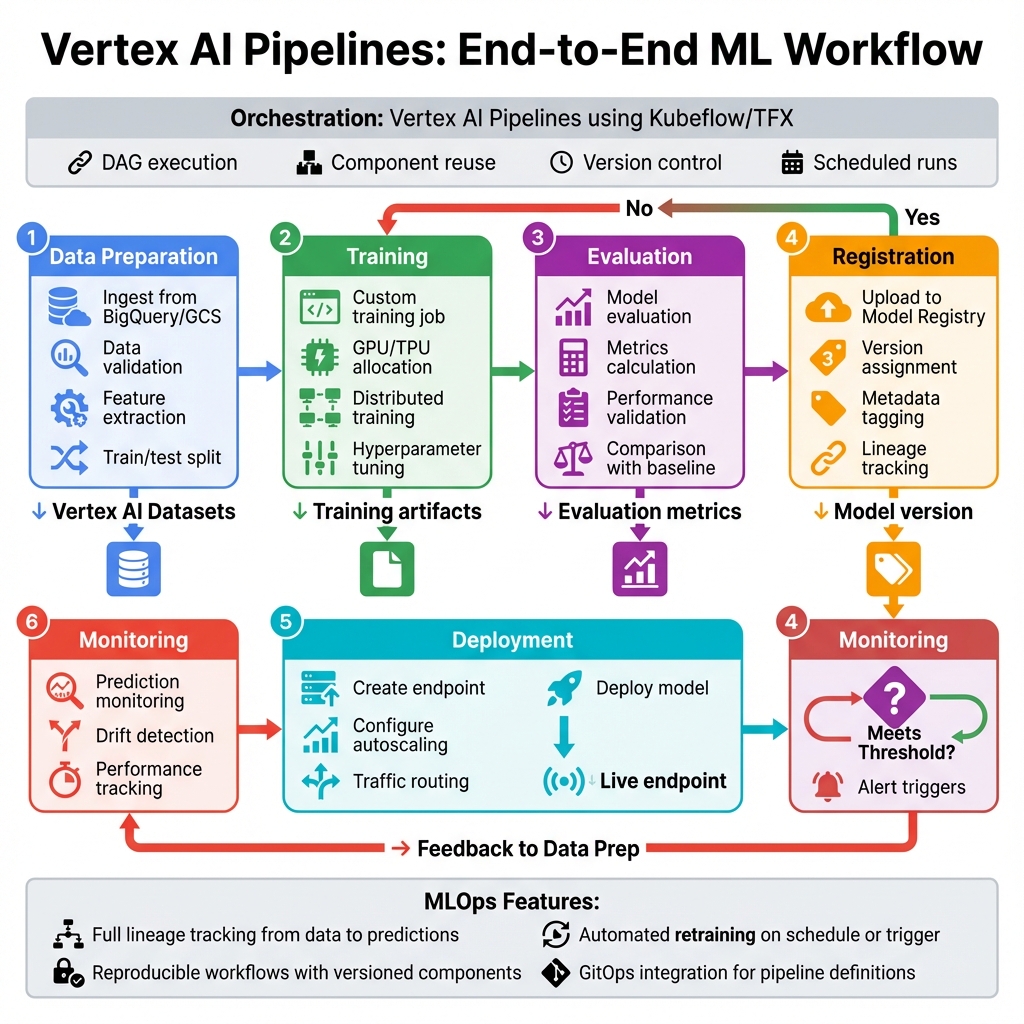
Vertex AI consolidates Google’s ML offerings into a unified platform with consistent APIs and tooling. The architecture spans the entire ML lifecycle: data preparation with Vertex AI Datasets, feature engineering with Feature Store, model training with AutoML or custom containers, deployment with Vertex AI Endpoints, and monitoring with Model Monitoring. This integration eliminates the fragmentation common in DIY ML platforms.

Training infrastructure scales automatically from single GPUs to distributed clusters with thousands of accelerators. Vertex AI supports NVIDIA GPUs (T4, V100, A100) and Google’s TPUs for large-scale training. Custom training jobs run in managed containers, supporting any ML framework—TensorFlow, PyTorch, JAX, or custom implementations. Pre-built containers for popular frameworks simplify deployment while custom containers provide unlimited flexibility.
Vertex AI Pipelines orchestrates ML workflows using Kubeflow Pipelines or TFX, providing reproducibility, versioning, and lineage tracking. Pipelines integrate with Vertex AI’s managed services—training, prediction, feature store—while supporting custom components for specialized processing. This enables GitOps-style ML workflows where pipeline definitions are version-controlled and changes trigger automated retraining.
Feature Store and Data Management
Vertex AI Feature Store provides a centralized repository for ML features, solving the critical challenge of feature consistency between training and serving. Features are defined once and served consistently across batch training and online inference, eliminating training-serving skew that plagues many ML systems. The Feature Store supports both batch ingestion from BigQuery and streaming updates for real-time features.
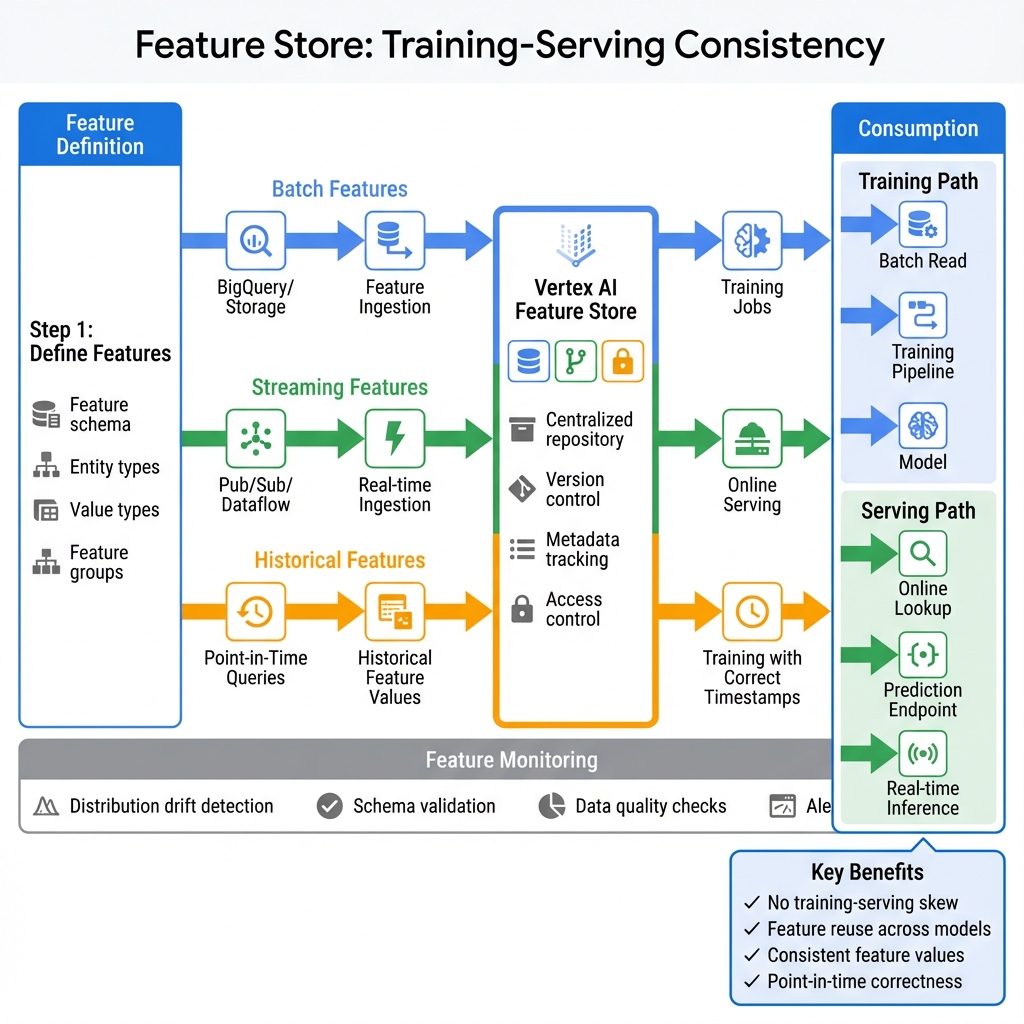
Feature engineering at scale leverages BigQuery ML and Dataflow for transformation pipelines. Point-in-time correctness ensures training data reflects the feature values available at prediction time, preventing data leakage. Feature monitoring tracks distribution drift, alerting when production features deviate from training distributions—a leading indicator of model degradation.
Vertex AI Datasets manage training data with versioning and lineage tracking. Datasets support structured data (BigQuery, CSV), images, video, and text, with automatic data validation and statistics. Managed datasets integrate with AutoML for no-code model training and with custom training for full control over data preprocessing.
Generative AI with Vertex AI GenAI Studio
Vertex AI GenAI Studio brings Google’s foundation models—Gemini 2.0 Flash, Gemini Pro, PaLM 2, Codey, and Imagen—into a unified development environment. The studio enables prompt design, model tuning, deployment, and monitoring for generative AI applications. This integrated approach accelerates LLMOps from experimentation to production.
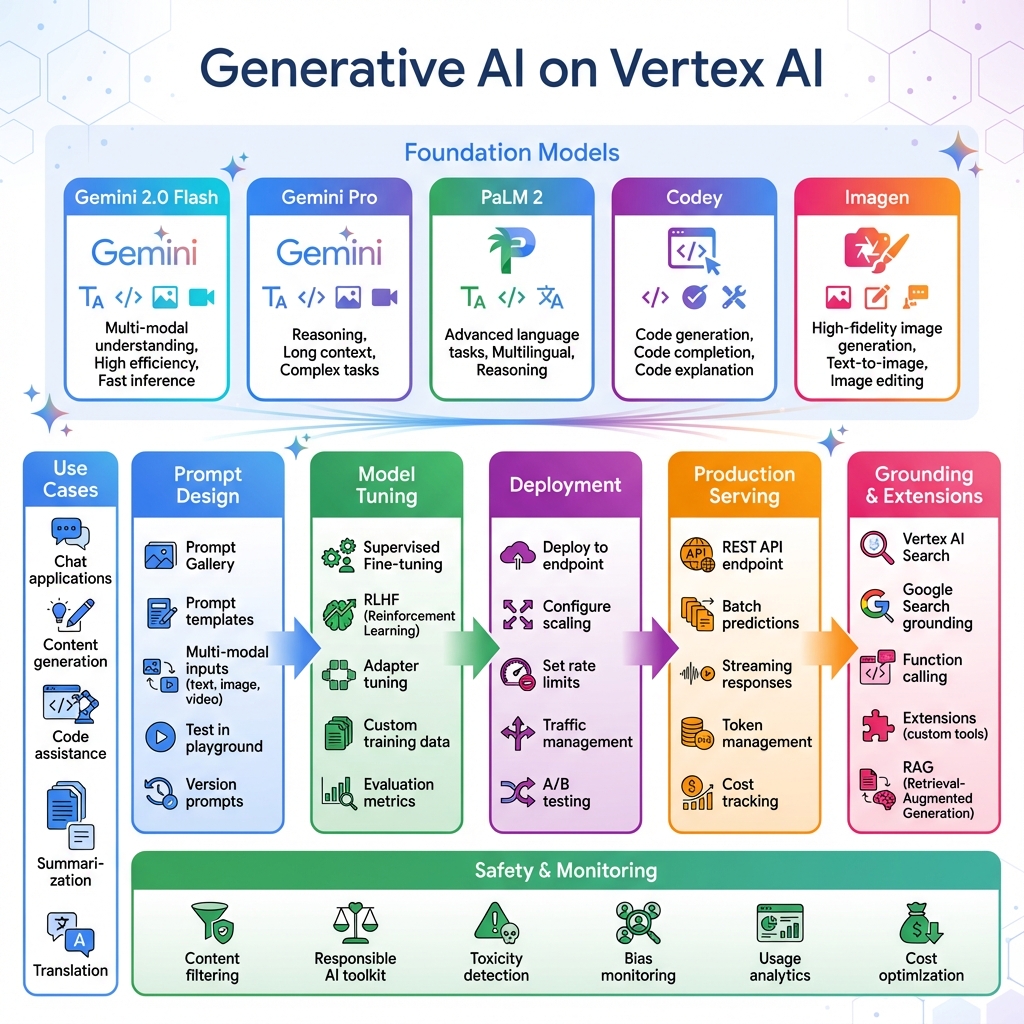
Grounding capabilities connect foundation models to external knowledge sources via Vertex AI Search or Google Search, enabling RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation) patterns. Function calling allows models to invoke custom tools and APIs, extending capabilities beyond text generation. The Responsible AI toolkit provides content filtering, toxicity detection, and bias monitoring to ensure safe generative AI deployments.
Production Terraform Configuration
Infrastructure as code ensures reproducible, version-controlled deployments of Vertex AI resources. Here’s how the production infrastructure components work together:
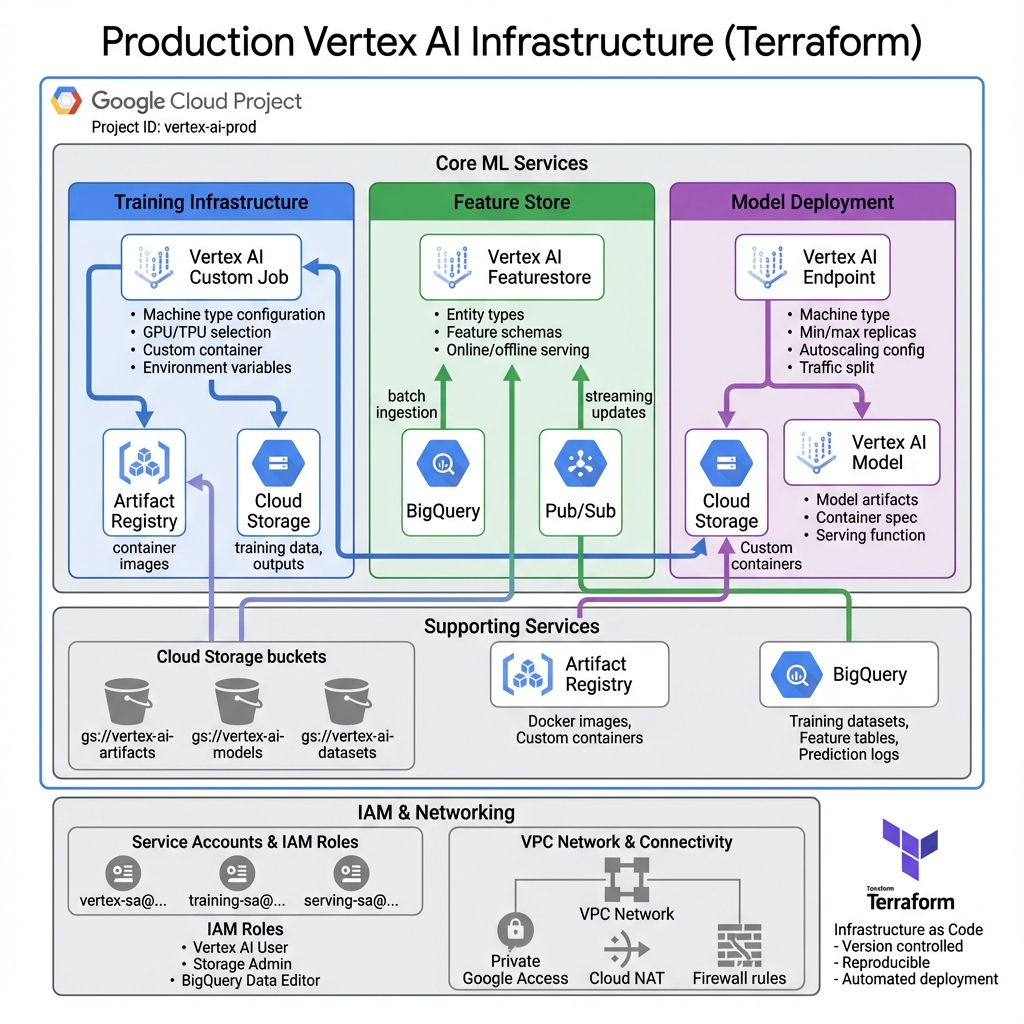
Here’s a comprehensive Terraform configuration for Vertex AI infrastructure including endpoints, feature store, and model monitoring:
# Vertex AI Enterprise Configuration
terraform {
required_version = ">= 1.5.0"
required_providers {
google = {
source = "hashicorp/google"
version = "~> 5.0"
}
}
}
variable "project_id" {
type = string
}
variable "region" {
type = string
default = "us-central1"
}
# Feature Store for ML features
resource "google_vertex_ai_featurestore" "main" {
name = "production_features"
region = var.region
online_serving_config {
fixed_node_count = 2
}
force_destroy = false
labels = {
environment = "production"
}
}
# Feature Store Entity Type
resource "google_vertex_ai_featurestore_entitytype" "users" {
name = "users"
featurestore = google_vertex_ai_featurestore.main.id
monitoring_config {
snapshot_analysis {
disabled = false
}
numerical_threshold_config {
value = 0.3
}
categorical_threshold_config {
value = 0.3
}
}
labels = {
entity = "user"
}
}
# Model endpoint for serving
resource "google_vertex_ai_endpoint" "prediction" {
name = "prediction-endpoint"
display_name = "Production Prediction Endpoint"
location = var.region
network = "projects/${var.project_id}/global/networks/default"
labels = {
environment = "production"
model = "recommendation"
}
}
# Service account for Vertex AI
resource "google_service_account" "vertex_sa" {
account_id = "vertex-ai-sa"
display_name = "Vertex AI Service Account"
}
# IAM roles for Vertex AI
resource "google_project_iam_member" "vertex_roles" {
for_each = toset([
"roles/aiplatform.user",
"roles/bigquery.dataEditor",
"roles/storage.objectAdmin"
])
project = var.project_id
role = each.value
member = "serviceAccount:${google_service_account.vertex_sa.email}"
}
# Cloud Storage bucket for artifacts
resource "google_storage_bucket" "ml_artifacts" {
name = "${var.project_id}-ml-artifacts"
location = var.region
uniform_bucket_level_access = true
versioning {
enabled = true
}
lifecycle_rule {
condition {
age = 90
}
action {
type = "Delete"
}
}
}
Cost Management and MLOps Best Practices
Vertex AI pricing varies by service: training costs depend on machine type and duration, prediction costs on requests and compute, and Feature Store on storage and serving nodes. For training, use preemptible VMs for fault-tolerant jobs to reduce costs by up to 80%. Spot instances work well for hyperparameter tuning where individual trial failures are acceptable.
Endpoint autoscaling prevents over-provisioning while maintaining latency SLAs. Configure min replicas based on baseline traffic and max replicas for peak loads. Use traffic splitting for gradual rollouts—deploy new models with 5-10% traffic initially, monitoring prediction quality before full rollout. Model versioning in Vertex AI Model Registry enables instant rollback if issues arise.
Implement CI/CD for ML with Vertex AI Pipelines. Pipeline definitions in version control trigger automated retraining when code or data changes. Model evaluation gates prevent deploying models that don’t meet quality thresholds. Metadata tracking provides full lineage from training data through deployed model, essential for debugging and compliance.
Key Takeaways and Best Practices
Vertex AI excels for organizations seeking a unified ML platform that scales from experimentation to production. Here’s how to succeed with Vertex AI in production:
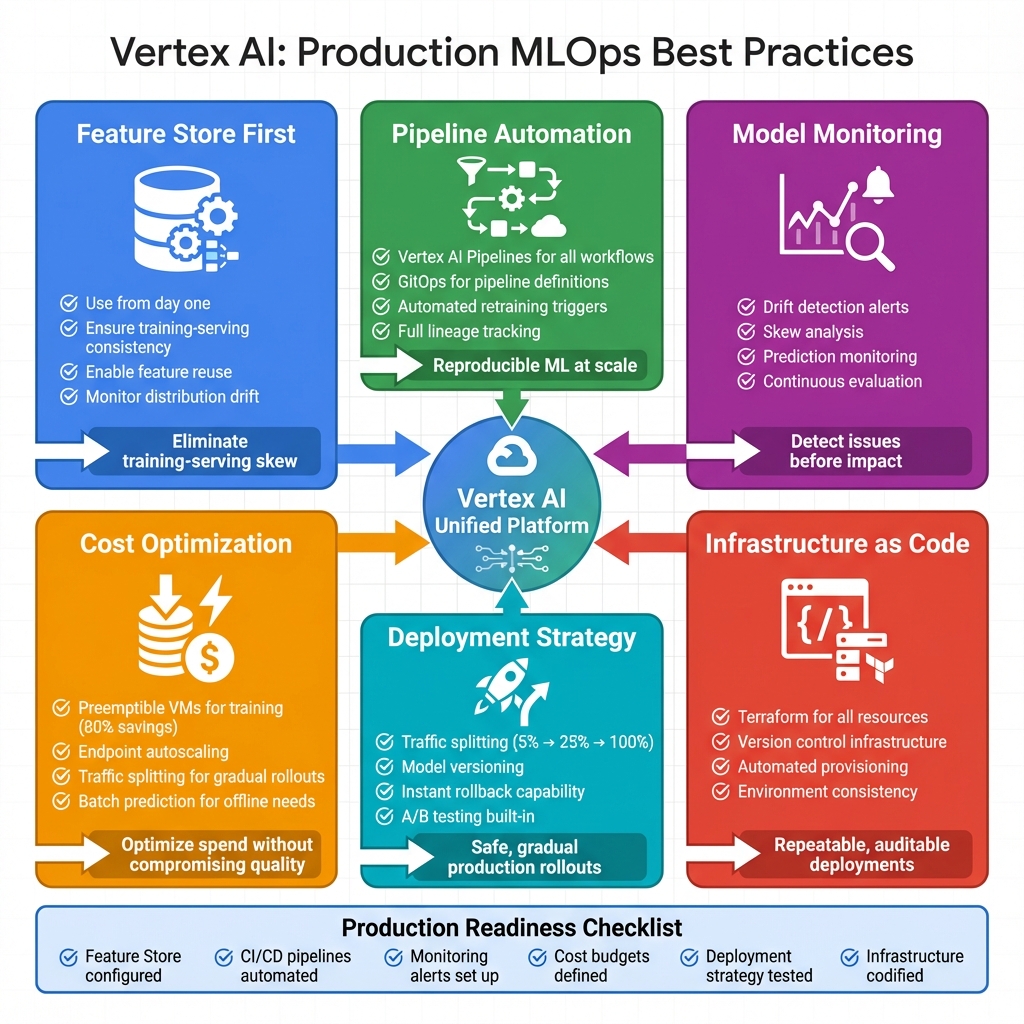
- ✅ Feature Store First – Use from day one to ensure training-serving consistency and enable feature reuse across models
- ✅ Pipeline Automation – Implement Vertex AI Pipelines for reproducible, automated ML workflows with proper versioning and lineage tracking
- ✅ Model Monitoring – Configure drift detection to identify issues before they impact business metrics
- ✅ Cost Optimization – Use preemptible VMs for training (80% savings), endpoint autoscaling, and batch prediction for offline workloads
- ✅ Safe Deployments – Use traffic splitting for gradual rollouts and maintain model versions for instant rollback capability
- ✅ Infrastructure as Code – Terraform all resources for version control, reproducibility, and automated provisioning
The Terraform and Python examples provided here establish patterns for production-ready Vertex AI deployments that support the full ML lifecycle from data preparation through model monitoring. Start with Feature Store to eliminate training-serving skew, build pipelines for automation, and implement comprehensive monitoring before models impact production traffic.
Have you deployed models on Vertex AI? Share your experiences on GitHub or LinkedIn.
Discover more from C4: Container, Code, Cloud & Context
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.