Introduction: Feature engineering remains the most impactful activity in machine learning, often determining model success more than algorithm selection. This comprehensive guide explores production feature engineering patterns, from feature stores and versioning to automated feature generation and real-time feature serving. After building feature platforms across multiple organizations, I’ve learned that success depends on treating features as first-class products with proper versioning, documentation, and governance. Organizations should invest in feature infrastructure early, establishing patterns for feature computation, storage, and serving that scale with growing ML adoption.
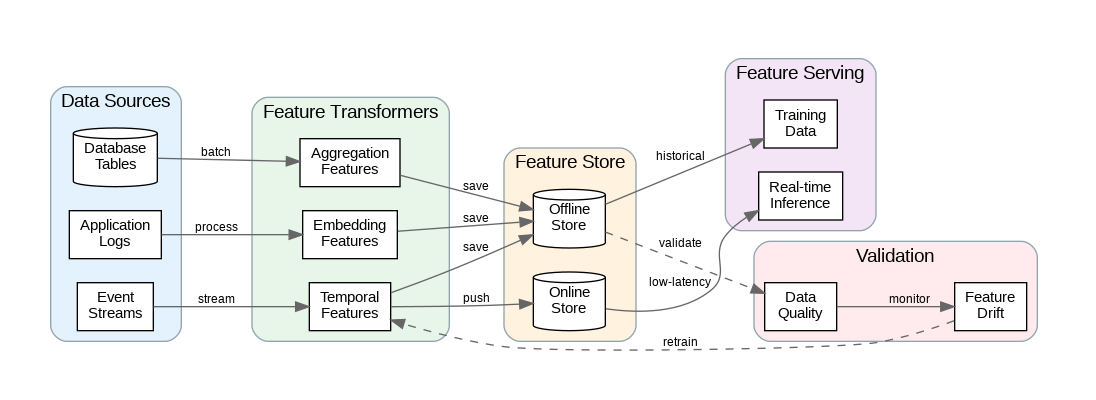
Feature Store Architecture
Feature stores provide centralized infrastructure for feature management, addressing the challenge of feature reuse across teams and models. Without a feature store, organizations duplicate feature engineering effort, create inconsistent feature definitions, and struggle with training-serving skew. A well-designed feature store enables feature discovery, ensures consistency between training and inference, and accelerates model development.
The dual-database architecture separates offline and online feature storage. Offline stores (data warehouses, object storage) hold historical feature values for training, supporting time-travel queries to reconstruct point-in-time feature sets. Online stores (Redis, DynamoDB) serve features with low latency for real-time inference, typically storing only the latest feature values per entity.
Feature computation pipelines transform raw data into features through batch and streaming processes. Batch pipelines compute features on historical data, running on schedules or triggered by data arrival. Streaming pipelines compute features in real-time from event streams, enabling features that reflect the latest state. Many features require both computation modes—batch for historical backfill and streaming for real-time updates.
Feature Engineering Patterns
Temporal features capture time-based patterns essential for many ML applications. Rolling aggregations (7-day average, 30-day sum) smooth noise and reveal trends. Lag features provide historical context for time-series prediction. Time-since features measure recency of events. Careful handling of temporal features prevents data leakage—ensure features only use information available at prediction time.
Aggregation features summarize entity behavior across related records. Count features track activity frequency. Statistical features (mean, median, standard deviation) characterize distributions. Ratio features compare related quantities. Design aggregations at multiple granularities—hourly, daily, weekly—to capture patterns at different time scales.
Embedding features represent categorical variables in continuous vector spaces. Pre-trained embeddings from language models capture semantic similarity for text features. Learned embeddings from collaborative filtering encode user and item relationships. Entity embeddings trained on tabular data capture complex categorical interactions that one-hot encoding misses.
Python Implementation: Feature Engineering Platform
Here’s a comprehensive implementation demonstrating production feature engineering patterns:
"""Production Feature Engineering Platform"""
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
from typing import Dict, List, Any, Optional, Callable, Union
from dataclasses import dataclass, field
from datetime import datetime, timedelta
from abc import ABC, abstractmethod
import hashlib
import json
import logging
from functools import wraps
import redis
from concurrent.futures import ThreadPoolExecutor
import pyarrow.parquet as pq
logging.basicConfig(level=logging.INFO)
logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
# ==================== Feature Definitions ====================
@dataclass
class FeatureDefinition:
"""Definition of a feature with metadata."""
name: str
description: str
entity: str # e.g., "user", "product", "transaction"
dtype: str
computation_type: str # "batch", "streaming", "on_demand"
dependencies: List[str] = field(default_factory=list)
ttl_seconds: Optional[int] = None
tags: List[str] = field(default_factory=list)
owner: str = "data-engineering"
@property
def feature_id(self) -> str:
"""Generate unique feature identifier."""
return f"{self.entity}__{self.name}"
def to_dict(self) -> Dict[str, Any]:
"""Convert to dictionary for serialization."""
return {
"name": self.name,
"description": self.description,
"entity": self.entity,
"dtype": self.dtype,
"computation_type": self.computation_type,
"dependencies": self.dependencies,
"ttl_seconds": self.ttl_seconds,
"tags": self.tags,
"owner": self.owner,
"feature_id": self.feature_id
}
@dataclass
class FeatureValue:
"""A computed feature value."""
feature_id: str
entity_id: str
value: Any
timestamp: datetime
version: str
def to_dict(self) -> Dict[str, Any]:
return {
"feature_id": self.feature_id,
"entity_id": self.entity_id,
"value": self.value,
"timestamp": self.timestamp.isoformat(),
"version": self.version
}
# ==================== Feature Transformers ====================
class FeatureTransformer(ABC):
"""Base class for feature transformers."""
@abstractmethod
def transform(self, df: pd.DataFrame) -> pd.DataFrame:
"""Transform input data to compute features."""
pass
@abstractmethod
def get_feature_definitions(self) -> List[FeatureDefinition]:
"""Return definitions for features this transformer produces."""
pass
class TemporalFeatureTransformer(FeatureTransformer):
"""Compute temporal/time-based features."""
def __init__(
self,
entity_col: str,
timestamp_col: str,
value_col: str,
windows: List[int] = [7, 14, 30],
aggregations: List[str] = ["mean", "sum", "count", "std"]
):
self.entity_col = entity_col
self.timestamp_col = timestamp_col
self.value_col = value_col
self.windows = windows
self.aggregations = aggregations
def transform(self, df: pd.DataFrame) -> pd.DataFrame:
"""Compute rolling window features."""
df = df.copy()
df[self.timestamp_col] = pd.to_datetime(df[self.timestamp_col])
df = df.sort_values([self.entity_col, self.timestamp_col])
features = []
for window in self.windows:
for agg in self.aggregations:
feature_name = f"{self.value_col}_{window}d_{agg}"
# Compute rolling aggregation per entity
rolling = df.groupby(self.entity_col)[self.value_col].transform(
lambda x: x.rolling(window=window, min_periods=1).agg(agg)
)
df[feature_name] = rolling
features.append(feature_name)
# Add lag features
for lag in [1, 7, 14]:
lag_name = f"{self.value_col}_lag_{lag}d"
df[lag_name] = df.groupby(self.entity_col)[self.value_col].shift(lag)
features.append(lag_name)
# Add time-since features
df["days_since_first"] = df.groupby(self.entity_col)[self.timestamp_col].transform(
lambda x: (x - x.min()).dt.days
)
return df
def get_feature_definitions(self) -> List[FeatureDefinition]:
"""Generate feature definitions for all computed features."""
definitions = []
for window in self.windows:
for agg in self.aggregations:
definitions.append(FeatureDefinition(
name=f"{self.value_col}_{window}d_{agg}",
description=f"{window}-day {agg} of {self.value_col}",
entity=self.entity_col,
dtype="float64",
computation_type="batch",
tags=["temporal", "aggregation"]
))
return definitions
class AggregationFeatureTransformer(FeatureTransformer):
"""Compute aggregation features across related records."""
def __init__(
self,
entity_col: str,
group_cols: List[str],
value_cols: List[str],
aggregations: Dict[str, List[str]]
):
self.entity_col = entity_col
self.group_cols = group_cols
self.value_cols = value_cols
self.aggregations = aggregations
def transform(self, df: pd.DataFrame) -> pd.DataFrame:
"""Compute aggregation features."""
result = df.copy()
for value_col in self.value_cols:
aggs = self.aggregations.get(value_col, ["mean", "sum", "count"])
for agg in aggs:
feature_name = f"{value_col}_{agg}_by_{'_'.join(self.group_cols)}"
agg_values = df.groupby(self.group_cols)[value_col].transform(agg)
result[feature_name] = agg_values
return result
def get_feature_definitions(self) -> List[FeatureDefinition]:
definitions = []
for value_col in self.value_cols:
aggs = self.aggregations.get(value_col, ["mean", "sum", "count"])
for agg in aggs:
definitions.append(FeatureDefinition(
name=f"{value_col}_{agg}_by_{'_'.join(self.group_cols)}",
description=f"{agg} of {value_col} grouped by {self.group_cols}",
entity=self.entity_col,
dtype="float64",
computation_type="batch",
tags=["aggregation"]
))
return definitions
class RatioFeatureTransformer(FeatureTransformer):
"""Compute ratio features between columns."""
def __init__(
self,
entity_col: str,
ratios: List[Dict[str, str]] # [{"numerator": "col1", "denominator": "col2", "name": "ratio_name"}]
):
self.entity_col = entity_col
self.ratios = ratios
def transform(self, df: pd.DataFrame) -> pd.DataFrame:
result = df.copy()
for ratio in self.ratios:
num = ratio["numerator"]
denom = ratio["denominator"]
name = ratio.get("name", f"{num}_to_{denom}_ratio")
# Avoid division by zero
result[name] = np.where(
result[denom] != 0,
result[num] / result[denom],
0
)
return result
def get_feature_definitions(self) -> List[FeatureDefinition]:
return [
FeatureDefinition(
name=ratio.get("name", f"{ratio['numerator']}_to_{ratio['denominator']}_ratio"),
description=f"Ratio of {ratio['numerator']} to {ratio['denominator']}",
entity=self.entity_col,
dtype="float64",
computation_type="batch",
tags=["ratio"]
)
for ratio in self.ratios
]
# ==================== Feature Store ====================
class FeatureStore:
"""Central feature store for managing features."""
def __init__(
self,
offline_store_path: str,
online_store_url: str = "redis://localhost:6379"
):
self.offline_store_path = offline_store_path
self.online_store = redis.from_url(online_store_url, decode_responses=True)
self.registry: Dict[str, FeatureDefinition] = {}
self.transformers: Dict[str, FeatureTransformer] = {}
def register_feature(self, definition: FeatureDefinition):
"""Register a feature definition."""
self.registry[definition.feature_id] = definition
logger.info(f"Registered feature: {definition.feature_id}")
def register_transformer(self, name: str, transformer: FeatureTransformer):
"""Register a feature transformer."""
self.transformers[name] = transformer
# Auto-register feature definitions
for definition in transformer.get_feature_definitions():
self.register_feature(definition)
def compute_features(
self,
transformer_name: str,
df: pd.DataFrame,
save_offline: bool = True,
push_online: bool = False
) -> pd.DataFrame:
"""Compute features using registered transformer."""
if transformer_name not in self.transformers:
raise ValueError(f"Unknown transformer: {transformer_name}")
transformer = self.transformers[transformer_name]
result = transformer.transform(df)
if save_offline:
self._save_to_offline_store(result, transformer_name)
if push_online:
self._push_to_online_store(result, transformer)
return result
def _save_to_offline_store(self, df: pd.DataFrame, name: str):
"""Save features to offline store (Parquet)."""
timestamp = datetime.now().strftime("%Y%m%d_%H%M%S")
path = f"{self.offline_store_path}/{name}/{timestamp}.parquet"
# In production, use cloud storage
df.to_parquet(path, index=False)
logger.info(f"Saved features to offline store: {path}")
def _push_to_online_store(self, df: pd.DataFrame, transformer: FeatureTransformer):
"""Push latest feature values to online store."""
definitions = transformer.get_feature_definitions()
feature_names = [d.name for d in definitions]
entity_col = definitions[0].entity if definitions else "entity_id"
for _, row in df.iterrows():
entity_id = str(row.get(entity_col, ""))
for feature_name in feature_names:
if feature_name in row:
key = f"feature:{entity_col}:{entity_id}:{feature_name}"
value = json.dumps({
"value": float(row[feature_name]) if pd.notna(row[feature_name]) else None,
"timestamp": datetime.now().isoformat()
})
# Set with TTL if defined
definition = self.registry.get(f"{entity_col}__{feature_name}")
ttl = definition.ttl_seconds if definition else None
if ttl:
self.online_store.setex(key, ttl, value)
else:
self.online_store.set(key, value)
logger.info(f"Pushed {len(df)} entities to online store")
def get_online_features(
self,
entity: str,
entity_ids: List[str],
feature_names: List[str]
) -> pd.DataFrame:
"""Retrieve features from online store."""
results = []
for entity_id in entity_ids:
row = {"entity_id": entity_id}
for feature_name in feature_names:
key = f"feature:{entity}:{entity_id}:{feature_name}"
value = self.online_store.get(key)
if value:
data = json.loads(value)
row[feature_name] = data.get("value")
else:
row[feature_name] = None
results.append(row)
return pd.DataFrame(results)
def get_historical_features(
self,
entity: str,
entity_ids: List[str],
feature_names: List[str],
timestamp: datetime
) -> pd.DataFrame:
"""Retrieve point-in-time features from offline store."""
# In production, query data warehouse with time-travel
# This is a simplified implementation
all_features = []
for transformer_name, transformer in self.transformers.items():
definitions = transformer.get_feature_definitions()
matching_features = [
d.name for d in definitions
if d.name in feature_names and d.entity == entity
]
if matching_features:
# Load from parquet files
import glob
files = glob.glob(f"{self.offline_store_path}/{transformer_name}/*.parquet")
if files:
df = pd.read_parquet(files[-1]) # Latest file
df = df[df[entity].isin(entity_ids)]
all_features.append(df[[entity] + matching_features])
if all_features:
result = all_features[0]
for df in all_features[1:]:
result = result.merge(df, on=entity, how="outer")
return result
return pd.DataFrame()
# ==================== Feature Pipeline ====================
class FeaturePipeline:
"""Orchestrates feature computation pipelines."""
def __init__(self, feature_store: FeatureStore):
self.feature_store = feature_store
self.steps: List[Dict[str, Any]] = []
def add_step(
self,
name: str,
transformer: FeatureTransformer,
input_source: str,
output_mode: str = "offline" # "offline", "online", "both"
):
"""Add a step to the pipeline."""
self.feature_store.register_transformer(name, transformer)
self.steps.append({
"name": name,
"transformer": transformer,
"input_source": input_source,
"output_mode": output_mode
})
def run(self, input_data: Dict[str, pd.DataFrame]) -> Dict[str, pd.DataFrame]:
"""Execute the feature pipeline."""
results = {}
for step in self.steps:
name = step["name"]
source = step["input_source"]
output_mode = step["output_mode"]
logger.info(f"Running pipeline step: {name}")
if source in input_data:
df = input_data[source]
elif source in results:
df = results[source]
else:
raise ValueError(f"Unknown input source: {source}")
result = self.feature_store.compute_features(
transformer_name=name,
df=df,
save_offline=output_mode in ["offline", "both"],
push_online=output_mode in ["online", "both"]
)
results[name] = result
logger.info(f"Step {name} completed: {len(result)} rows, {len(result.columns)} columns")
return results
# ==================== Feature Validation ====================
class FeatureValidator:
"""Validates feature quality and consistency."""
def __init__(self):
self.checks: List[Callable] = []
def add_check(self, check: Callable):
"""Add a validation check."""
self.checks.append(check)
def validate(self, df: pd.DataFrame, feature_names: List[str]) -> Dict[str, Any]:
"""Run all validation checks."""
results = {
"passed": True,
"checks": [],
"summary": {}
}
for feature in feature_names:
if feature not in df.columns:
results["checks"].append({
"feature": feature,
"check": "exists",
"passed": False,
"message": "Feature not found in dataframe"
})
results["passed"] = False
continue
# Null check
null_rate = df[feature].isnull().mean()
null_passed = null_rate < 0.5
results["checks"].append({
"feature": feature,
"check": "null_rate",
"passed": null_passed,
"value": null_rate
})
if not null_passed:
results["passed"] = False
# Numeric range check
if pd.api.types.is_numeric_dtype(df[feature]):
has_inf = np.isinf(df[feature].dropna()).any()
results["checks"].append({
"feature": feature,
"check": "no_infinity",
"passed": not has_inf
})
if has_inf:
results["passed"] = False
# Statistics
results["summary"][feature] = {
"mean": df[feature].mean(),
"std": df[feature].std(),
"min": df[feature].min(),
"max": df[feature].max(),
"null_rate": null_rate
}
return results
# ==================== Example Usage ====================
def run_feature_pipeline():
"""Example feature pipeline execution."""
# Create sample data
np.random.seed(42)
n_records = 10000
transactions = pd.DataFrame({
"user_id": np.random.randint(1, 100, n_records),
"transaction_date": pd.date_range("2024-01-01", periods=n_records, freq="H"),
"amount": np.random.exponential(100, n_records),
"category": np.random.choice(["food", "transport", "entertainment", "shopping"], n_records),
"merchant_id": np.random.randint(1, 50, n_records)
})
# Initialize feature store
feature_store = FeatureStore(
offline_store_path="/tmp/feature_store",
online_store_url="redis://localhost:6379"
)
# Create pipeline
pipeline = FeaturePipeline(feature_store)
# Add temporal features
pipeline.add_step(
name="temporal_features",
transformer=TemporalFeatureTransformer(
entity_col="user_id",
timestamp_col="transaction_date",
value_col="amount",
windows=[7, 14, 30],
aggregations=["mean", "sum", "count"]
),
input_source="transactions",
output_mode="both"
)
# Add ratio features
pipeline.add_step(
name="ratio_features",
transformer=RatioFeatureTransformer(
entity_col="user_id",
ratios=[
{"numerator": "amount_7d_sum", "denominator": "amount_30d_sum", "name": "weekly_to_monthly_ratio"},
{"numerator": "amount_7d_count", "denominator": "amount_30d_count", "name": "weekly_to_monthly_txn_ratio"}
]
),
input_source="temporal_features",
output_mode="offline"
)
# Run pipeline
results = pipeline.run({"transactions": transactions})
# Validate features
validator = FeatureValidator()
validation = validator.validate(
results["ratio_features"],
["amount_7d_mean", "amount_30d_sum", "weekly_to_monthly_ratio"]
)
print(f"Validation passed: {validation['passed']}")
print(f"Feature summary: {json.dumps(validation['summary'], indent=2)}")
# Retrieve online features
online_features = feature_store.get_online_features(
entity="user_id",
entity_ids=["1", "2", "3"],
feature_names=["amount_7d_mean", "amount_30d_sum"]
)
print(f"Online features:\n{online_features}")
if __name__ == "__main__":
run_feature_pipeline()Real-Time Feature Serving
Low-latency feature serving enables real-time ML applications like fraud detection, recommendations, and dynamic pricing. Design online stores for sub-millisecond reads using in-memory databases like Redis or purpose-built feature stores. Pre-compute and cache features where possible, falling back to on-demand computation only when necessary.
Feature freshness requirements vary by use case. Some features can tolerate staleness of hours or days; others require real-time updates. Design streaming pipelines for features requiring immediate updates, using Kafka or Kinesis to process events and update online stores. Balance freshness requirements against computational cost and complexity.
Training-serving consistency prevents subtle bugs where models see different feature values during training versus inference. Use the same feature computation code for both paths. Implement point-in-time joins for training data to reconstruct features as they existed at prediction time. Monitor feature distributions in production to detect drift from training data.
Key Takeaways and Best Practices
Feature engineering at scale requires treating features as products with proper infrastructure, versioning, and governance. Invest in feature stores to enable reuse and ensure consistency. Design transformers that produce well-documented, validated features. Implement both batch and real-time computation paths based on freshness requirements.
The code examples provided here establish patterns for production feature platforms. Start with batch feature computation and offline storage, then add real-time capabilities as use cases demand. In the next article, we'll explore real-time data streaming with Apache Kafka and Flink, building on these feature engineering foundations.
Discover more from C4: Container, Code, Cloud & Context
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.