Introduction: Function calling transforms LLMs from text generators into action-taking agents. Instead of just describing what to do, the model can actually do it—query databases, call APIs, execute code, and interact with external systems. OpenAI’s function calling (now called “tools”) and similar features from Anthropic and others let you define available functions, and the model intelligently decides when and how to call them. This guide covers implementing function calling from basic tool definitions to complex multi-step workflows, parallel function execution, and production patterns for reliable tool use.
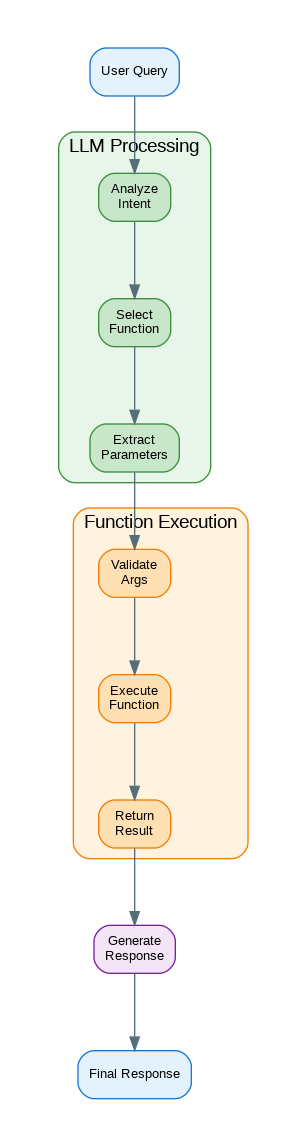
Basic Function Calling with OpenAI
from openai import OpenAI
import json
client = OpenAI()
# Define tools
tools = [
{
"type": "function",
"function": {
"name": "get_weather",
"description": "Get the current weather for a location",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"location": {
"type": "string",
"description": "City and state, e.g., San Francisco, CA"
},
"unit": {
"type": "string",
"enum": ["celsius", "fahrenheit"],
"description": "Temperature unit"
}
},
"required": ["location"]
}
}
},
{
"type": "function",
"function": {
"name": "search_products",
"description": "Search for products in the catalog",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"query": {
"type": "string",
"description": "Search query"
},
"category": {
"type": "string",
"enum": ["electronics", "clothing", "books", "home"]
},
"max_price": {
"type": "number",
"description": "Maximum price filter"
}
},
"required": ["query"]
}
}
}
]
# Implement the actual functions
def get_weather(location: str, unit: str = "fahrenheit") -> dict:
"""Simulated weather API call."""
# In production, call actual weather API
return {
"location": location,
"temperature": 72 if unit == "fahrenheit" else 22,
"unit": unit,
"conditions": "sunny"
}
def search_products(query: str, category: str = None, max_price: float = None) -> list:
"""Simulated product search."""
# In production, query actual database
return [
{"name": f"{query} Pro", "price": 99.99, "category": category or "electronics"},
{"name": f"{query} Basic", "price": 49.99, "category": category or "electronics"}
]
# Function dispatcher
def execute_function(name: str, arguments: dict):
"""Execute a function by name."""
functions = {
"get_weather": get_weather,
"search_products": search_products
}
if name not in functions:
raise ValueError(f"Unknown function: {name}")
return functions[name](**arguments)
# Complete conversation with function calling
def chat_with_tools(user_message: str) -> str:
"""Chat with automatic function calling."""
messages = [{"role": "user", "content": user_message}]
# First call - model may request function calls
response = client.chat.completions.create(
model="gpt-4o",
messages=messages,
tools=tools,
tool_choice="auto" # or "none", "required", or specific function
)
assistant_message = response.choices[0].message
# Check if model wants to call functions
if assistant_message.tool_calls:
messages.append(assistant_message)
# Execute each function call
for tool_call in assistant_message.tool_calls:
function_name = tool_call.function.name
arguments = json.loads(tool_call.function.arguments)
# Execute function
result = execute_function(function_name, arguments)
# Add result to messages
messages.append({
"role": "tool",
"tool_call_id": tool_call.id,
"content": json.dumps(result)
})
# Get final response with function results
final_response = client.chat.completions.create(
model="gpt-4o",
messages=messages,
tools=tools
)
return final_response.choices[0].message.content
return assistant_message.content
# Usage
result = chat_with_tools("What's the weather in New York?")
print(result)Parallel Function Calls
import asyncio
from concurrent.futures import ThreadPoolExecutor
def chat_with_parallel_tools(user_message: str) -> str:
"""Handle parallel function calls efficiently."""
messages = [{"role": "user", "content": user_message}]
response = client.chat.completions.create(
model="gpt-4o",
messages=messages,
tools=tools,
tool_choice="auto",
parallel_tool_calls=True # Enable parallel calls
)
assistant_message = response.choices[0].message
if assistant_message.tool_calls:
messages.append(assistant_message)
# Execute functions in parallel
with ThreadPoolExecutor(max_workers=5) as executor:
futures = {}
for tool_call in assistant_message.tool_calls:
function_name = tool_call.function.name
arguments = json.loads(tool_call.function.arguments)
future = executor.submit(execute_function, function_name, arguments)
futures[tool_call.id] = future
# Collect results
for tool_call in assistant_message.tool_calls:
result = futures[tool_call.id].result()
messages.append({
"role": "tool",
"tool_call_id": tool_call.id,
"content": json.dumps(result)
})
# Get final response
final_response = client.chat.completions.create(
model="gpt-4o",
messages=messages,
tools=tools
)
return final_response.choices[0].message.content
return assistant_message.content
# Async version
async def async_chat_with_tools(user_message: str) -> str:
"""Async function calling with parallel execution."""
from openai import AsyncOpenAI
async_client = AsyncOpenAI()
messages = [{"role": "user", "content": user_message}]
response = await async_client.chat.completions.create(
model="gpt-4o",
messages=messages,
tools=tools,
tool_choice="auto"
)
assistant_message = response.choices[0].message
if assistant_message.tool_calls:
messages.append(assistant_message)
# Execute functions concurrently
async def execute_async(tool_call):
function_name = tool_call.function.name
arguments = json.loads(tool_call.function.arguments)
# Run sync function in thread pool
loop = asyncio.get_event_loop()
result = await loop.run_in_executor(
None, execute_function, function_name, arguments
)
return tool_call.id, result
results = await asyncio.gather(*[
execute_async(tc) for tc in assistant_message.tool_calls
])
for tool_call_id, result in results:
messages.append({
"role": "tool",
"tool_call_id": tool_call_id,
"content": json.dumps(result)
})
final_response = await async_client.chat.completions.create(
model="gpt-4o",
messages=messages,
tools=tools
)
return final_response.choices[0].message.content
return assistant_message.contentFunction Calling with Claude
import anthropic
client = anthropic.Anthropic()
# Define tools for Claude
claude_tools = [
{
"name": "get_weather",
"description": "Get the current weather for a location",
"input_schema": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"location": {
"type": "string",
"description": "City and state, e.g., San Francisco, CA"
},
"unit": {
"type": "string",
"enum": ["celsius", "fahrenheit"],
"description": "Temperature unit"
}
},
"required": ["location"]
}
}
]
def chat_with_claude_tools(user_message: str) -> str:
"""Function calling with Claude."""
messages = [{"role": "user", "content": user_message}]
response = client.messages.create(
model="claude-3-5-sonnet-20241022",
max_tokens=1024,
tools=claude_tools,
messages=messages
)
# Check for tool use
if response.stop_reason == "tool_use":
# Find tool use blocks
tool_uses = [block for block in response.content if block.type == "tool_use"]
# Add assistant response
messages.append({"role": "assistant", "content": response.content})
# Execute tools and add results
tool_results = []
for tool_use in tool_uses:
result = execute_function(tool_use.name, tool_use.input)
tool_results.append({
"type": "tool_result",
"tool_use_id": tool_use.id,
"content": json.dumps(result)
})
messages.append({"role": "user", "content": tool_results})
# Get final response
final_response = client.messages.create(
model="claude-3-5-sonnet-20241022",
max_tokens=1024,
tools=claude_tools,
messages=messages
)
return final_response.content[0].text
return response.content[0].textMulti-Step Tool Workflows
class ToolAgent:
"""Agent that can execute multi-step tool workflows."""
def __init__(self, tools: list, max_iterations: int = 10):
self.tools = tools
self.max_iterations = max_iterations
self.tool_functions = {}
def register_function(self, name: str, func: callable):
"""Register a function implementation."""
self.tool_functions[name] = func
def run(self, user_message: str) -> str:
"""Run agent until completion or max iterations."""
messages = [{"role": "user", "content": user_message}]
for iteration in range(self.max_iterations):
response = client.chat.completions.create(
model="gpt-4o",
messages=messages,
tools=self.tools,
tool_choice="auto"
)
assistant_message = response.choices[0].message
messages.append(assistant_message)
# Check if done (no more tool calls)
if not assistant_message.tool_calls:
return assistant_message.content
# Execute all tool calls
for tool_call in assistant_message.tool_calls:
function_name = tool_call.function.name
arguments = json.loads(tool_call.function.arguments)
print(f"[Iteration {iteration + 1}] Calling {function_name}({arguments})")
try:
result = self.tool_functions[function_name](**arguments)
except Exception as e:
result = {"error": str(e)}
messages.append({
"role": "tool",
"tool_call_id": tool_call.id,
"content": json.dumps(result)
})
return "Max iterations reached without completion"
# Example: Research agent with multiple tools
research_tools = [
{
"type": "function",
"function": {
"name": "web_search",
"description": "Search the web for information",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"query": {"type": "string", "description": "Search query"}
},
"required": ["query"]
}
}
},
{
"type": "function",
"function": {
"name": "read_url",
"description": "Read content from a URL",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"url": {"type": "string", "description": "URL to read"}
},
"required": ["url"]
}
}
},
{
"type": "function",
"function": {
"name": "save_note",
"description": "Save a research note",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"title": {"type": "string"},
"content": {"type": "string"}
},
"required": ["title", "content"]
}
}
}
]
agent = ToolAgent(research_tools)
agent.register_function("web_search", lambda query: {"results": [f"Result for {query}"]})
agent.register_function("read_url", lambda url: {"content": f"Content from {url}"})
agent.register_function("save_note", lambda title, content: {"saved": True})
result = agent.run("Research the latest developments in quantum computing and save a summary")Error Handling and Validation
from pydantic import BaseModel, ValidationError
from typing import Optional
# Define function schemas with Pydantic
class WeatherParams(BaseModel):
location: str
unit: Optional[str] = "fahrenheit"
class ProductSearchParams(BaseModel):
query: str
category: Optional[str] = None
max_price: Optional[float] = None
def safe_execute_function(name: str, arguments: dict) -> dict:
"""Execute function with validation and error handling."""
schemas = {
"get_weather": WeatherParams,
"search_products": ProductSearchParams
}
try:
# Validate arguments
if name in schemas:
validated = schemas[name](**arguments)
arguments = validated.model_dump()
# Execute function
result = execute_function(name, arguments)
return {"success": True, "result": result}
except ValidationError as e:
return {
"success": False,
"error": "Invalid arguments",
"details": e.errors()
}
except Exception as e:
return {
"success": False,
"error": str(e)
}
def chat_with_error_handling(user_message: str) -> str:
"""Chat with robust error handling for function calls."""
messages = [{"role": "user", "content": user_message}]
response = client.chat.completions.create(
model="gpt-4o",
messages=messages,
tools=tools,
tool_choice="auto"
)
assistant_message = response.choices[0].message
if assistant_message.tool_calls:
messages.append(assistant_message)
for tool_call in assistant_message.tool_calls:
function_name = tool_call.function.name
try:
arguments = json.loads(tool_call.function.arguments)
except json.JSONDecodeError:
arguments = {}
result = safe_execute_function(function_name, arguments)
messages.append({
"role": "tool",
"tool_call_id": tool_call.id,
"content": json.dumps(result)
})
final_response = client.chat.completions.create(
model="gpt-4o",
messages=messages,
tools=tools
)
return final_response.choices[0].message.content
return assistant_message.contentReferences
- OpenAI Function Calling: https://platform.openai.com/docs/guides/function-calling
- Anthropic Tool Use: https://docs.anthropic.com/claude/docs/tool-use
- LangChain Tools: https://python.langchain.com/docs/modules/tools/
Conclusion
Function calling bridges the gap between LLM intelligence and real-world action. Well-designed tools let models query databases, call APIs, execute code, and interact with any system you can wrap in a function. The key is clear function descriptions—the model needs to understand when and how to use each tool. Start with simple, single-purpose functions and clear parameter schemas. Add parallel execution for efficiency when tools are independent. Implement robust error handling because tools will fail. For complex workflows, build agent loops that iterate until the task is complete. Remember that function calling adds latency (extra API calls) and cost (more tokens for tool definitions and results), so design your tool set thoughtfully. The payoff is transforming your LLM from a text generator into a capable assistant that can actually get things done.
Discover more from Code, Cloud & Context
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.