Enterprise VPC design on Google Cloud requires balancing security, performance, and operational simplicity. This comprehensive guide covers Zero Trust architecture, global network design, VPC Service Controls, and hybrid connectivity patterns that meet the demands of modern enterprise workloads.
Zero Trust Network Architecture
Zero Trust assumes no implicit trust—every access request must be authenticated and authorized regardless of network location. Google Cloud provides native capabilities to implement Zero Trust through Identity-Aware Proxy (IAP), BeyondCorp Enterprise, and VPC Service Controls.
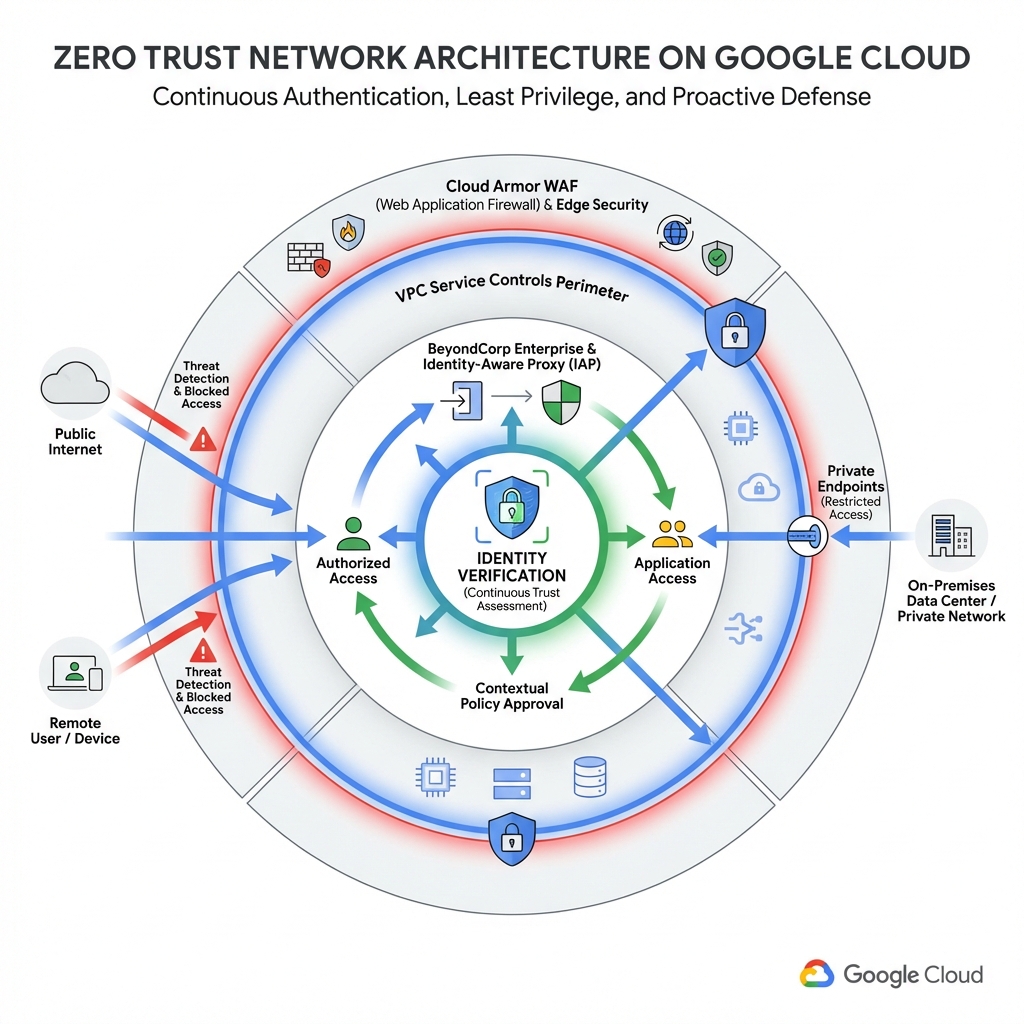
Identity-Aware Proxy (IAP)
IAP establishes a central authorization layer for applications accessed via HTTPS. Instead of relying on VPN, users authenticate with their Google identity, and IAP verifies their access rights before allowing the connection.
# Enable IAP for a backend service
gcloud compute backend-services update my-backend \
--iap=enabled \
--global
# Grant IAP access to users
gcloud projects add-iam-policy-binding my-project \
--member="user:developer@example.com" \
--role="roles/iap.httpsResourceAccessor"
# Grant access to a group
gcloud projects add-iam-policy-binding my-project \
--member="group:engineering@example.com" \
--role="roles/iap.httpsResourceAccessor"BeyondCorp Enterprise
BeyondCorp Enterprise extends Zero Trust to endpoints by evaluating device security posture. Access decisions consider device ownership, OS patch level, disk encryption, and screen lock status.
# Access Level definition for corporate devices
name: accessPolicies/123456789/accessLevels/corporate_devices
title: Corporate Managed Devices
basic:
conditions:
- devicePolicy:
requireCorpOwned: true
osConstraints:
- osType: DESKTOP_CHROME_OS
minimumVersion: "13904.0.0"
- osType: DESKTOP_MAC
minimumVersion: "12.0.0"
- osType: DESKTOP_WINDOWS
minimumVersion: "10.0.19041"
requireScreenlock: true
allowedEncryptionStatuses:
- ENCRYPTEDMobile device management (MDM) enrollment is required to evaluate device posture for mobile endpoints. Ensure your MDM solution is integrated with Google Cloud before enabling device-based access levels.
Global VPC Architecture
Google Cloud VPCs are global resources, meaning subnets in different regions can communicate without explicit peering. This enables simplified multi-region deployments with automatic failover and low-latency cross-region communication.
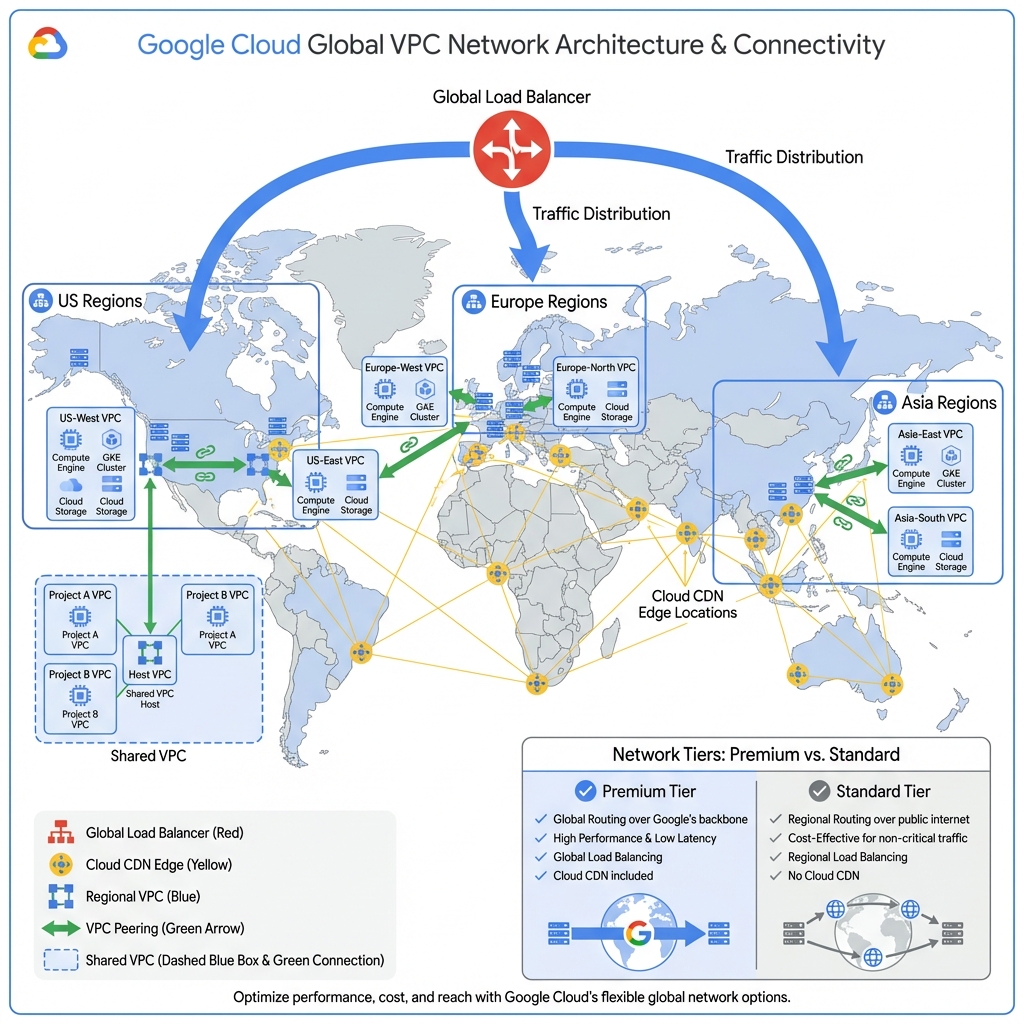
Premium vs Standard Network Tier
Premium Tier: Traffic enters Google’s network at the edge closest to the user and travels over Google’s private backbone. Provides lowest latency and highest reliability. Includes global load balancing with Cloud CDN.
Standard Tier: Traffic travels over the public internet before entering Google’s network at the region where your resources reside. Lower cost but higher latency and regional load balancing only.
# Terraform: Global VPC with regional subnets
resource "google_compute_network" "global_vpc" {
name = "enterprise-vpc"
auto_create_subnetworks = false
routing_mode = "GLOBAL"
}
# US subnet
resource "google_compute_subnetwork" "us_subnet" {
name = "us-central1-subnet"
ip_cidr_range = "10.0.0.0/20"
region = "us-central1"
network = google_compute_network.global_vpc.id
private_ip_google_access = true
log_config {
aggregation_interval = "INTERVAL_5_SEC"
flow_sampling = 0.5
metadata = "INCLUDE_ALL_METADATA"
}
}
# Europe subnet
resource "google_compute_subnetwork" "eu_subnet" {
name = "europe-west1-subnet"
ip_cidr_range = "10.1.0.0/20"
region = "europe-west1"
network = google_compute_network.global_vpc.id
private_ip_google_access = true
}
# Asia subnet
resource "google_compute_subnetwork" "asia_subnet" {
name = "asia-east1-subnet"
ip_cidr_range = "10.2.0.0/20"
region = "asia-east1"
network = google_compute_network.global_vpc.id
private_ip_google_access = true
}Global Load Balancing
Google’s Global HTTP(S) Load Balancer provides a single anycast IP address that routes users to the nearest healthy backend. Combined with Cloud CDN, it delivers sub-100ms response times globally.
# Create global load balancer with backends in multiple regions
# 1. Create health check
gcloud compute health-checks create http my-health-check \
--port=80 \
--request-path=/health
# 2. Create backend service
gcloud compute backend-services create my-backend \
--protocol=HTTP \
--health-checks=my-health-check \
--global \
--enable-cdn
# 3. Add regional instance groups
gcloud compute backend-services add-backend my-backend \
--instance-group=us-mig \
--instance-group-region=us-central1 \
--global
gcloud compute backend-services add-backend my-backend \
--instance-group=eu-mig \
--instance-group-region=europe-west1 \
--global
# 4. Create URL map and forwarding rule
gcloud compute url-maps create my-url-map --default-service=my-backend
gcloud compute target-http-proxies create my-proxy --url-map=my-url-map
gcloud compute forwarding-rules create my-lb \
--global \
--target-http-proxy=my-proxy \
--ports=80VPC Service Controls
VPC Service Controls create security perimeters around GCP resources to prevent data exfiltration. Even with valid IAM permissions, requests from outside the perimeter are blocked—critical for compliance with HIPAA, PCI-DSS, and GDPR.
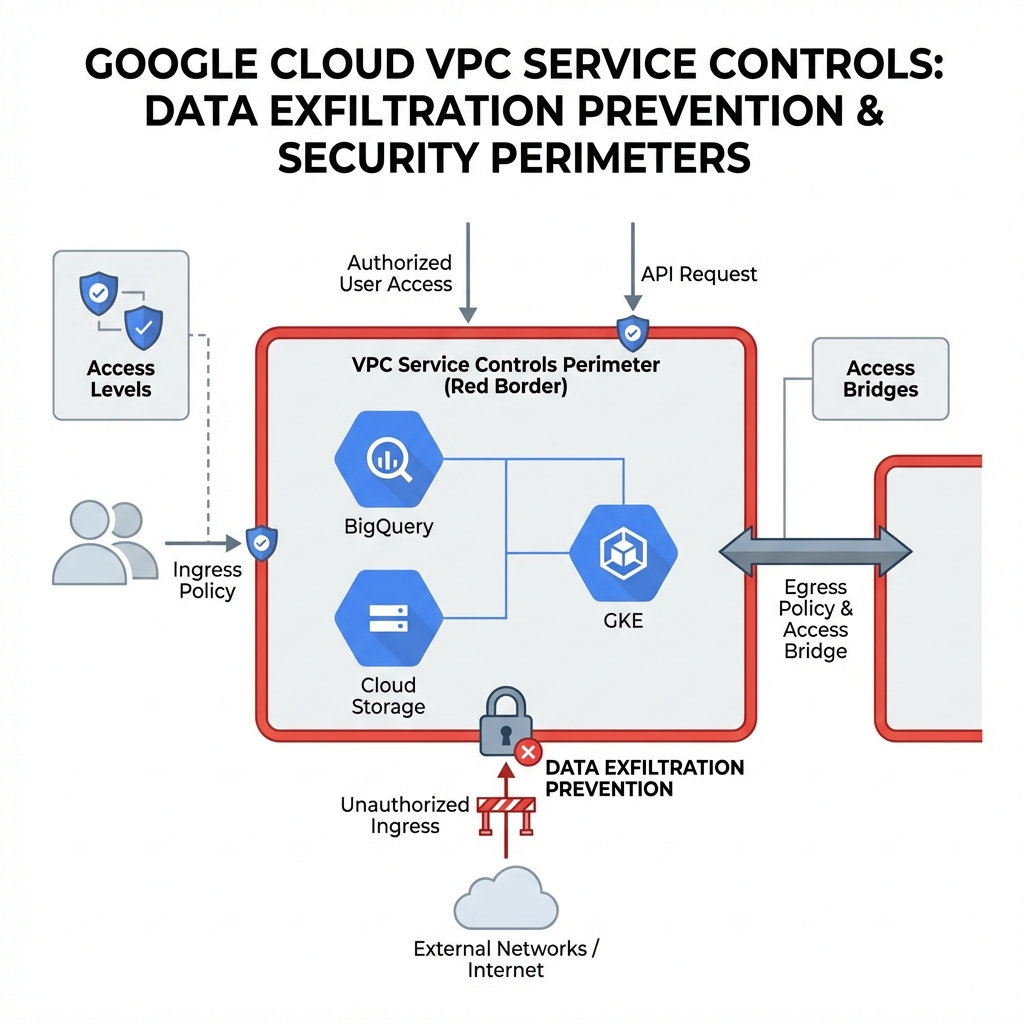
Creating a Service Perimeter
A service perimeter defines which projects and services are protected, and what network paths are allowed for access. Dry-run mode lets you test policies before enforcement.
# Create access policy (organization-level)
gcloud access-context-manager policies create \
--organization=123456789 \
--title="Enterprise Security Policy"
# Create service perimeter
gcloud access-context-manager perimeters create data_perimeter \
--policy=123456789 \
--title="Data Platform Perimeter" \
--resources=projects/12345,projects/67890 \
--restricted-services=bigquery.googleapis.com,storage.googleapis.com \
--access-levels=accessPolicies/123456789/accessLevels/corporate_network
# Enable in dry-run mode first
gcloud access-context-manager perimeters dry-run create data_perimeter \
--policy=123456789 \
--resources=projects/12345 \
--restricted-services=bigquery.googleapis.comAlways enable dry-run mode for 2-4 weeks before enforcing a perimeter. Monitor violation logs to identify legitimate access patterns that need access level exceptions.
Hybrid Connectivity
Connecting on-premises networks to GCP requires choosing between Cloud VPN and Cloud Interconnect based on bandwidth, latency, and reliability requirements.
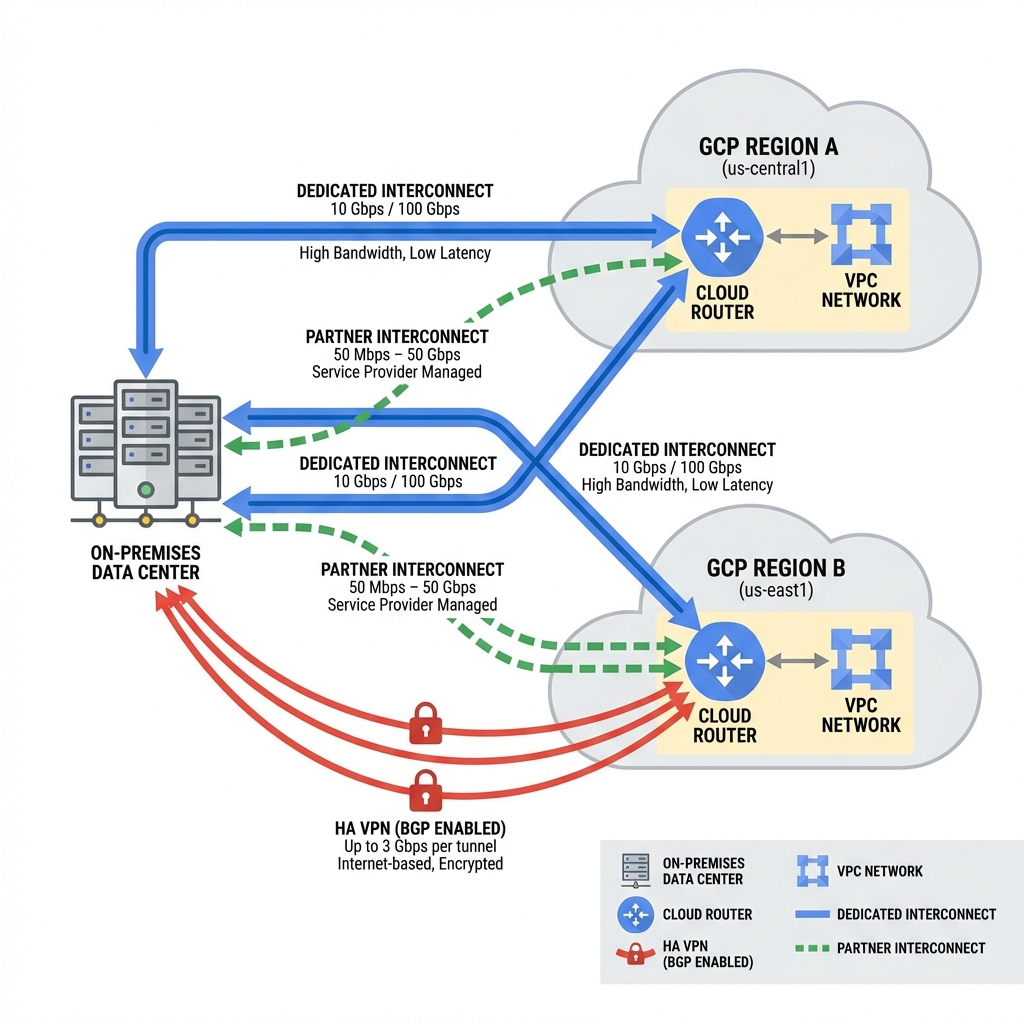
Connectivity Options Comparison
Choosing the right hybrid connectivity option depends on your bandwidth, latency, reliability, and cost requirements. The table below provides a detailed comparison.
| Feature | HA VPN | Partner Interconnect | Dedicated Interconnect |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bandwidth | Up to 3 Gbps/tunnel | 50 Mbps – 50 Gbps | 10 or 100 Gbps/link |
| Latency | Variable (internet) | Low | Lowest |
| SLA | 99.99% | 99.9% – 99.99% | 99.99% |
| Encryption | ✅ IPsec built-in | ❌ Add MACsec | ❌ Add MACsec |
| Setup Time | Minutes | Days–Weeks | Weeks–Months |
| Requirements | Internet only | Service provider | Colocation |
| Best For | Dev/test, backup | Mid-size production | Large enterprise |
Cloud VPN (HA VPN): Encrypted tunnels over the public internet. Ideal for getting started quickly or as backup connectivity. Deploy in HA configuration with two tunnels for 99.99% SLA.
Dedicated Interconnect: Physical connection at a Google colocation facility. Choose when you need guaranteed bandwidth and lowest latency. Requires 10 Gbps minimum commitment.
Partner Interconnect: Connection through a certified service provider. Best when you need better performance than VPN but can’t access a colocation facility. Scales from 50 Mbps to 50 Gbps.
Egress through Interconnect costs ~$0.02/GB vs ~$0.12/GB through internet. For data-heavy workloads, Interconnect often pays for itself in egress savings.
# Terraform: HA VPN with BGP
resource "google_compute_ha_vpn_gateway" "ha_gateway" {
name = "ha-vpn-gateway"
network = google_compute_network.global_vpc.id
region = "us-central1"
}
resource "google_compute_router" "vpn_router" {
name = "vpn-router"
region = "us-central1"
network = google_compute_network.global_vpc.id
bgp {
asn = 64512
advertise_mode = "CUSTOM"
advertised_groups = ["ALL_SUBNETS"]
advertised_ip_ranges {
range = "10.0.0.0/8"
}
}
}
resource "google_compute_vpn_tunnel" "tunnel1" {
name = "vpn-tunnel-1"
vpn_gateway = google_compute_ha_vpn_gateway.ha_gateway.id
peer_external_gateway = google_compute_external_vpn_gateway.peer.id
shared_secret = var.vpn_shared_secret
router = google_compute_router.vpn_router.id
vpn_gateway_interface = 0
peer_external_gateway_interface = 0
}
resource "google_compute_router_interface" "router_interface1" {
name = "interface-1"
router = google_compute_router.vpn_router.name
region = "us-central1"
ip_range = "169.254.0.1/30"
vpn_tunnel = google_compute_vpn_tunnel.tunnel1.name
}
resource "google_compute_router_peer" "peer1" {
name = "bgp-peer-1"
router = google_compute_router.vpn_router.name
region = "us-central1"
peer_ip_address = "169.254.0.2"
peer_asn = 65001
interface = google_compute_router_interface.router_interface1.name
}Firewall Rules and Policies
Google Cloud offers multiple layers of firewall protection. Understanding the hierarchy and when to use each type is essential for defense-in-depth security.
Firewall Rule Types
VPC Firewall Rules: The basic building block, applied at the project level. Rules are stateful—return traffic for allowed connections is automatically permitted.
Firewall Policies (Hierarchical): Organization or folder-level policies inherited by all child projects. Cannot be overridden by VPC-level rules—ideal for enforcing baseline security.
Network Firewall Policies: Regional or global policies attached to VPCs. Support advanced features like FQDN-based rules and geo-location matching.
Rule Priority and Evaluation
Rules are evaluated in priority order (0-65535, lower = higher priority). The first matching rule determines the action.
| Priority | Recommended Use | Example |
|---|---|---|
| 0–999 | Emergency blocks | Block attack IPs immediately |
| 1000–1999 | Org-wide deny rules | Block malicious IP ranges |
| 2000–2999 | Org-wide allow rules | Allow internal RFC1918 |
| 3000–9999 | Application rules | Allow HTTPS to web tier |
| 65535 | Implied deny | Deny all unmatched traffic |
Service-Based Firewall Rules
Use service accounts instead of IP ranges for more maintainable rules as infrastructure scales.
# Terraform: Service-based firewall rules
# Allow web tier to API tier using service accounts
resource "google_compute_firewall" "web_to_api" {
name = "allow-web-to-api"
network = google_compute_network.vpc.name
allow {
protocol = "tcp"
ports = ["8080", "443"]
}
source_service_accounts = [google_service_account.web_tier.email]
target_service_accounts = [google_service_account.api_tier.email]
priority = 3000
}
# Deny direct web to database (defense in depth)
resource "google_compute_firewall" "deny_web_to_db" {
name = "deny-web-to-db"
network = google_compute_network.vpc.name
deny {
protocol = "tcp"
ports = ["5432", "3306"]
}
source_service_accounts = [google_service_account.web_tier.email]
target_service_accounts = [google_service_account.db_tier.email]
priority = 2500
}Hierarchical Firewall Policies
Organization-level policies cannot be overridden by project admins—ensuring critical security controls remain in place. Understanding the evaluation order is essential for effective policy design.
Policy Evaluation Order
When traffic arrives at a VM, firewall rules are evaluated in a specific order. The first matching rule (allow or deny) determines the outcome.
| Order | Policy Type | Scope | Can Override? |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Hierarchical Firewall Policy (Org) | All projects in org | ❌ No |
| 2 | Hierarchical Firewall Policy (Folder) | Projects in folder | ❌ No |
| 3 | VPC Firewall Rules | Single VPC | ✅ Yes (by project admin) |
| 4 | Implied Rules | All VPCs | ❌ No |
Hierarchical policies use “goto_next” action: Unlike VPC rules, hierarchical policies can delegate to the next level. If no rule matches or all matching rules use “goto_next”, evaluation continues to VPC firewall rules.
Priority Enforcement Best Practices
Follow these guidelines when designing your firewall policy hierarchy:
| Best Practice | Description |
|---|---|
| 1. Deny first, allow later | Place deny rules at priorities 1000-1999 before allow rules at 2000+. This ensures malicious traffic is blocked before any allow rules can match. |
| 2. Reserve priority gaps | Leave gaps between priorities (e.g., 1000, 1100, 1200) so you can insert new rules without renumbering existing ones. |
| 3. Use goto_next sparingly | Only delegate to VPC rules when you explicitly want project admins to control specific traffic. Default to explicit allow/deny. |
| 4. Document rule purpose | Use descriptive names and add descriptions to every rule. Future admins (including you) will thank you. |
| 5. Audit regularly | Review firewall logs and remove unused rules. Stale rules increase attack surface and complexity. |
| 6. Test in dry-run | Use Firewall Insights to simulate policy changes before applying them to production. |
Example: Layered Security Policy
# Terraform: Complete hierarchical policy example
# Organization-level policy - enforced everywhere
resource "google_compute_firewall_policy" "org_policy" {
short_name = "org-security-baseline"
parent = "organizations/123456789"
description = "Baseline security controls for entire organization"
}
# Priority 100: Block known threat actors (highest priority)
resource "google_compute_firewall_policy_rule" "block_threats" {
firewall_policy = google_compute_firewall_policy.org_policy.id
priority = 100
action = "deny"
direction = "INGRESS"
description = "Block traffic from known malicious IP ranges"
match {
src_ip_ranges = var.threat_intel_ip_ranges # Updated from threat feed
layer4_configs { ip_protocol = "all" }
}
}
# Priority 1000: Block high-risk ports org-wide
resource "google_compute_firewall_policy_rule" "block_risky_ports" {
firewall_policy = google_compute_firewall_policy.org_policy.id
priority = 1000
action = "deny"
direction = "INGRESS"
description = "Block direct access to database ports from internet"
match {
src_ip_ranges = ["0.0.0.0/0"]
layer4_configs {
ip_protocol = "tcp"
ports = ["3306", "5432", "1433", "27017", "6379"] # MySQL, PG, MSSQL, Mongo, Redis
}
}
}
# Priority 2000: Allow internal communication
resource "google_compute_firewall_policy_rule" "allow_internal" {
firewall_policy = google_compute_firewall_policy.org_policy.id
priority = 2000
action = "allow"
direction = "INGRESS"
description = "Allow all internal RFC1918 traffic"
match {
src_ip_ranges = ["10.0.0.0/8", "172.16.0.0/12", "192.168.0.0/16"]
layer4_configs { ip_protocol = "all" }
}
}
# Priority 3000: Delegate web traffic to VPC rules
resource "google_compute_firewall_policy_rule" "delegate_web" {
firewall_policy = google_compute_firewall_policy.org_policy.id
priority = 3000
action = "goto_next" # Let VPC rules decide
direction = "INGRESS"
description = "Delegate HTTP/HTTPS rules to project VPC firewalls"
match {
src_ip_ranges = ["0.0.0.0/0"]
layer4_configs {
ip_protocol = "tcp"
ports = ["80", "443"]
}
}
}
# Apply to organization
resource "google_compute_firewall_policy_association" "org" {
firewall_policy = google_compute_firewall_policy.org_policy.id
attachment_target = "organizations/123456789"
name = "org-baseline-association"
}A deny at org level CANNOT be overridden by an allow at folder, project, or VPC level. This is by design—it ensures security teams can enforce baseline controls that developers cannot bypass. Plan your policy hierarchy carefully and test changes in a sandbox first.
Key Takeaways
- ✅ Implement Zero Trust – Use IAP and BeyondCorp for identity-centric access control
- ✅ Leverage global VPC – Take advantage of cross-region communication without explicit peering
- ✅ Choose Premium Tier for production – Lower latency and global load balancing are worth the cost
- ✅ Enable VPC Service Controls – Critical for preventing data exfiltration in regulated industries
- ✅ Use HA VPN for redundancy – Always deploy VPN tunnels in pairs for failover
- ✅ Apply hierarchical firewall policies – Enforce baseline security at the organization level
Conclusion
Designing enterprise VPC networks on Google Cloud requires a thoughtful approach to security, global reach, and hybrid connectivity. Zero Trust architecture with IAP and VPC Service Controls provides defense in depth. Global VPCs with Premium Tier networking deliver low-latency performance worldwide. And hybrid connectivity options from HA VPN to Dedicated Interconnect enable seamless extension of on-premises networks to the cloud. The patterns and code examples in this guide provide a foundation for building secure, scalable enterprise networks on GCP.
References
- BeyondCorp Enterprise Documentation
- VPC Service Controls
- Cloud Interconnect Documentation
- Cloud VPN Overview
- Cloud Load Balancing
Discover more from C4: Container, Code, Cloud & Context
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.