AWS provides a comprehensive suite of storage and database services for every workload. This guide covers S3 object storage, EBS block storage, RDS relational databases, DynamoDB NoSQL, and Aurora—with production-ready code examples.
This is Part 3 of a 6-part series covering AWS Cloud Platform.
AWS Storage Services Overview
AWS offers three types of storage: object (S3), block (EBS), and file (EFS/FSx). Each is optimized for different access patterns and use cases.
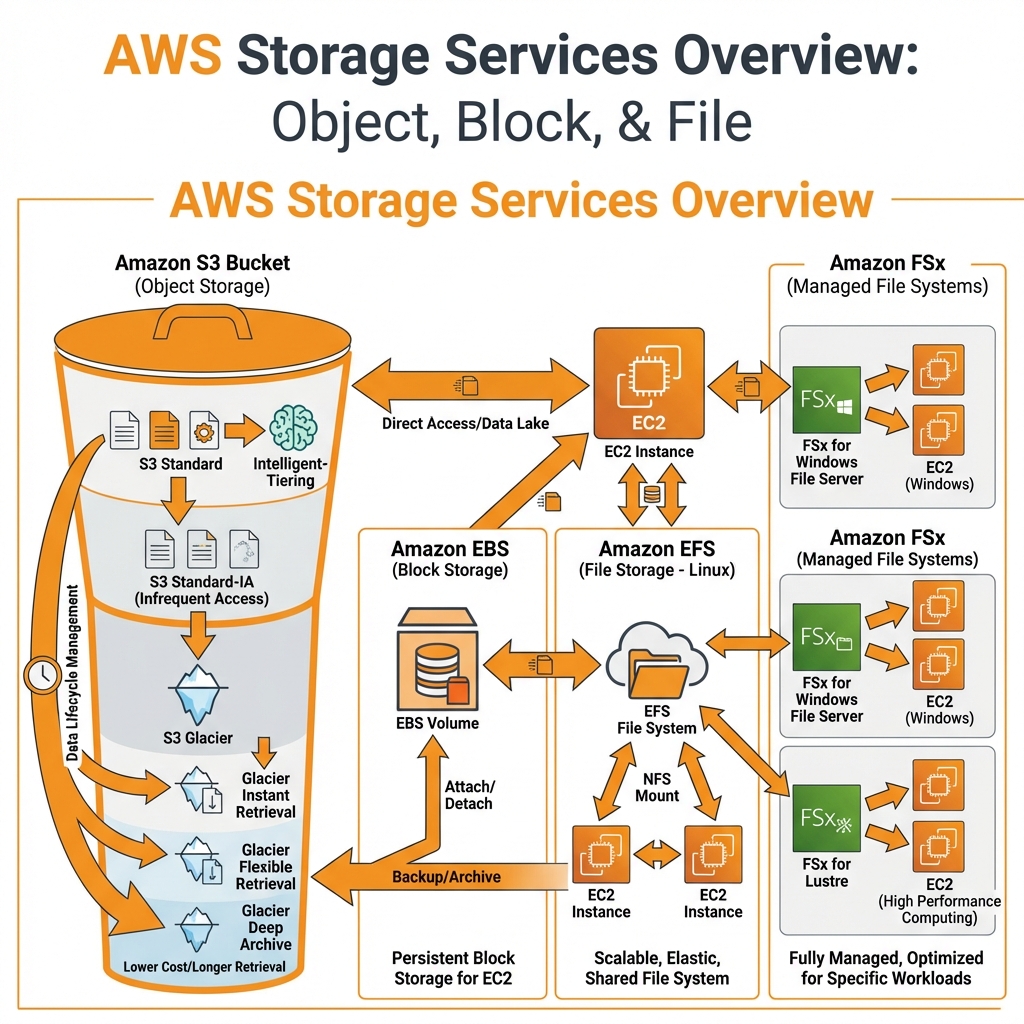
Amazon S3 (Simple Storage Service)
S3 is AWS’s object storage service offering 11 9’s (99.999999999%) durability. It’s the foundation for data lakes, backups, static websites, and application assets.
S3 Storage Classes
| Storage Class | Use Case | Availability | Min Duration | Retrieval |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| S3 Standard | Frequently accessed data | 99.99% | None | Instant |
| S3 Intelligent-Tiering | Unknown/changing access | 99.9% | None | Instant |
| S3 Standard-IA | Infrequent access, fast retrieval | 99.9% | 30 days | Instant |
| S3 Glacier Instant | Archive with instant access | 99.9% | 90 days | Instant |
| S3 Glacier Flexible | Backup, archive (min/hours) | 99.99% | 90 days | 1 min – 12 hrs |
| S3 Glacier Deep Archive | Long-term archive (7+ years) | 99.99% | 180 days | 12-48 hrs |
S3 with AWS CDK
// AWS CDK: Production S3 bucket with best practices
import * as cdk from 'aws-cdk-lib';
import * as s3 from 'aws-cdk-lib/aws-s3';
import * as iam from 'aws-cdk-lib/aws-iam';
export class S3Stack extends cdk.Stack {
public readonly bucket: s3.Bucket;
constructor(scope: cdk.App, id: string, props?: cdk.StackProps) {
super(scope, id, props);
// Production bucket with security best practices
this.bucket = new s3.Bucket(this, 'DataBucket', {
bucketName: `data-${this.account}-${this.region}`,
// Security
encryption: s3.BucketEncryption.S3_MANAGED,
enforceSSL: true,
blockPublicAccess: s3.BlockPublicAccess.BLOCK_ALL,
// Versioning for data protection
versioned: true,
// Lifecycle rules for cost optimization
lifecycleRules: [
{
id: 'TransitionToIA',
transitions: [
{
storageClass: s3.StorageClass.INFREQUENT_ACCESS,
transitionAfter: cdk.Duration.days(30),
},
{
storageClass: s3.StorageClass.GLACIER,
transitionAfter: cdk.Duration.days(90),
},
],
},
{
id: 'DeleteOldVersions',
noncurrentVersionExpiration: cdk.Duration.days(365),
noncurrentVersionTransitions: [
{
storageClass: s3.StorageClass.GLACIER,
transitionAfter: cdk.Duration.days(30),
},
],
},
{
id: 'AbortIncompleteUploads',
abortIncompleteMultipartUploadAfter: cdk.Duration.days(7),
},
],
// Access logging
serverAccessLogsPrefix: 'access-logs/',
// Intelligent tiering for unpredictable access
intelligentTieringConfigurations: [
{
name: 'archive-config',
archiveAccessTierTime: cdk.Duration.days(90),
deepArchiveAccessTierTime: cdk.Duration.days(180),
},
],
});
// Cross-region replication (optional)
// this.bucket.addReplicationRule({...});
}
}S3 with Terraform
# Terraform: Production S3 bucket
resource "aws_s3_bucket" "data" {
bucket = "data-${data.aws_caller_identity.current.account_id}-${var.region}"
}
resource "aws_s3_bucket_versioning" "data" {
bucket = aws_s3_bucket.data.id
versioning_configuration {
status = "Enabled"
}
}
resource "aws_s3_bucket_server_side_encryption_configuration" "data" {
bucket = aws_s3_bucket.data.id
rule {
apply_server_side_encryption_by_default {
sse_algorithm = "AES256"
}
bucket_key_enabled = true
}
}
resource "aws_s3_bucket_public_access_block" "data" {
bucket = aws_s3_bucket.data.id
block_public_acls = true
block_public_policy = true
ignore_public_acls = true
restrict_public_buckets = true
}
resource "aws_s3_bucket_lifecycle_configuration" "data" {
bucket = aws_s3_bucket.data.id
rule {
id = "transition-to-ia"
status = "Enabled"
transition {
days = 30
storage_class = "STANDARD_IA"
}
transition {
days = 90
storage_class = "GLACIER"
}
noncurrent_version_transition {
noncurrent_days = 30
storage_class = "GLACIER"
}
noncurrent_version_expiration {
noncurrent_days = 365
}
}
}- Object size: 5 TB max (use multipart for >100 MB)
- 3,500 PUT/POST/DELETE and 5,500 GET per second per prefix
- Bucket names globally unique (first come, first served)
- Standard-IA: 128 KB minimum charge per object
- Glacier: 40 KB overhead + 8 KB metadata per object
- Data retrieval from Glacier costs extra (plan ahead!)
AWS Database Services
AWS offers purpose-built databases for different workloads: relational (RDS, Aurora), NoSQL (DynamoDB, DocumentDB), in-memory (ElastiCache), graph (Neptune), and time-series (Timestream).
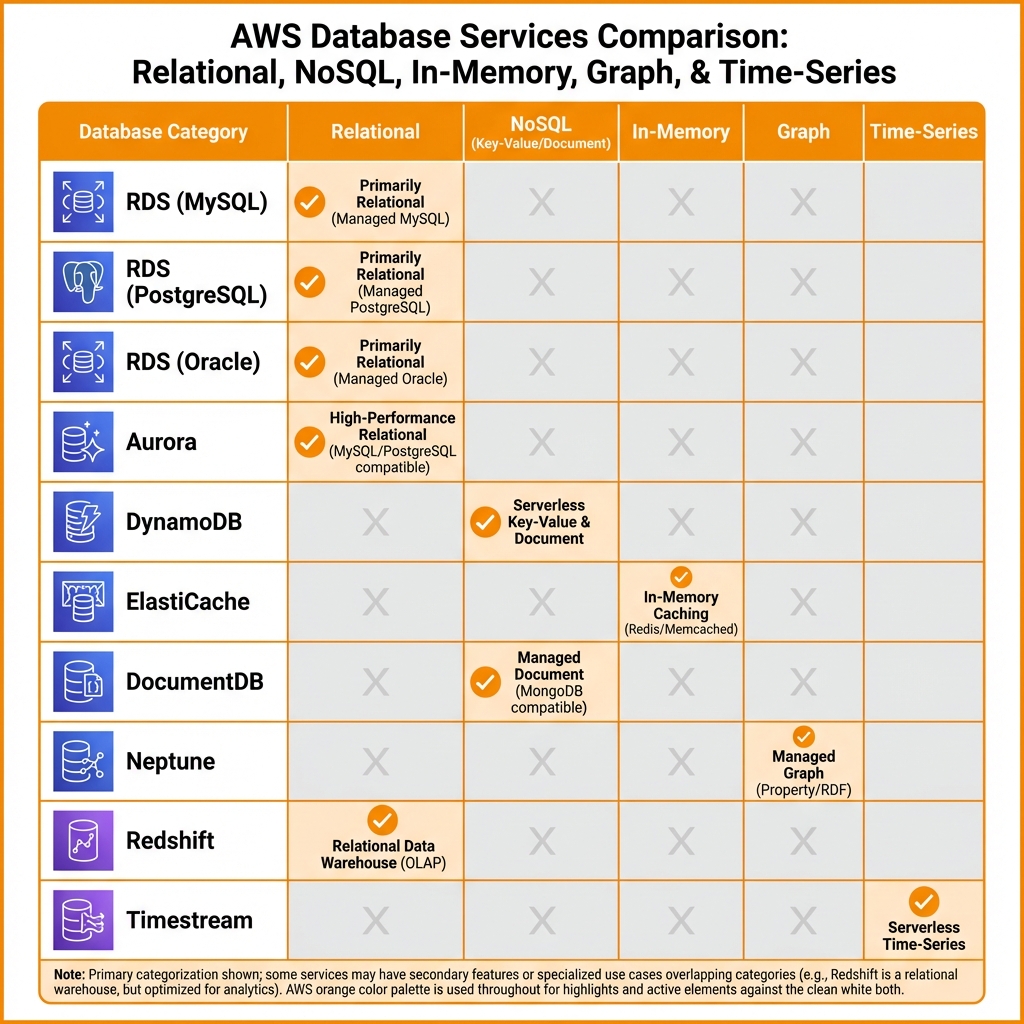
Amazon RDS (Relational Database Service)
RDS provides managed relational databases for MySQL, PostgreSQL, MariaDB, Oracle, and SQL Server. AWS handles backups, patching, and high availability.
RDS with AWS CDK
// AWS CDK: Production RDS PostgreSQL with Multi-AZ
import * as cdk from 'aws-cdk-lib';
import * as rds from 'aws-cdk-lib/aws-rds';
import * as ec2 from 'aws-cdk-lib/aws-ec2';
import * as secretsmanager from 'aws-cdk-lib/aws-secretsmanager';
export class RdsStack extends cdk.Stack {
constructor(scope: cdk.App, id: string, props?: cdk.StackProps) {
super(scope, id, props);
const vpc = ec2.Vpc.fromLookup(this, 'Vpc', { isDefault: false });
// Security group for database
const dbSg = new ec2.SecurityGroup(this, 'DbSg', {
vpc,
description: 'Security group for RDS',
allowAllOutbound: false,
});
// RDS PostgreSQL instance
const database = new rds.DatabaseInstance(this, 'Database', {
engine: rds.DatabaseInstanceEngine.postgres({
version: rds.PostgresEngineVersion.VER_15_4,
}),
instanceType: ec2.InstanceType.of(
ec2.InstanceClass.R6G,
ec2.InstanceSize.LARGE
),
vpc,
vpcSubnets: { subnetType: ec2.SubnetType.PRIVATE_ISOLATED },
securityGroups: [dbSg],
// High availability
multiAz: true,
// Storage
allocatedStorage: 100,
maxAllocatedStorage: 500, // Auto-scaling
storageType: rds.StorageType.GP3,
storageThroughput: 125, // GP3 throughput
// Credentials (auto-generated and stored in Secrets Manager)
credentials: rds.Credentials.fromGeneratedSecret('dbadmin', {
secretName: 'prod/rds/credentials',
}),
// Database settings
databaseName: 'appdb',
port: 5432,
// Backup & maintenance
backupRetention: cdk.Duration.days(30),
preferredBackupWindow: '03:00-04:00',
preferredMaintenanceWindow: 'sun:04:00-sun:05:00',
deleteAutomatedBackups: false,
// Monitoring
enablePerformanceInsights: true,
performanceInsightRetention: rds.PerformanceInsightRetention.MONTHS_1,
cloudwatchLogsExports: ['postgresql', 'upgrade'],
// Protection
deletionProtection: true,
removalPolicy: cdk.RemovalPolicy.RETAIN,
});
// Output connection info
new cdk.CfnOutput(this, 'DbEndpoint', {
value: database.dbInstanceEndpointAddress,
});
new cdk.CfnOutput(this, 'SecretArn', {
value: database.secret?.secretArn || '',
});
}
}Amazon DynamoDB
DynamoDB is a fully managed NoSQL database delivering single-digit millisecond latency at any scale. It’s ideal for high-throughput applications with predictable access patterns.
DynamoDB with AWS CDK
// AWS CDK: DynamoDB table with GSI and auto-scaling
import * as cdk from 'aws-cdk-lib';
import * as dynamodb from 'aws-cdk-lib/aws-dynamodb';
export class DynamoStack extends cdk.Stack {
constructor(scope: cdk.App, id: string, props?: cdk.StackProps) {
super(scope, id, props);
// DynamoDB table with on-demand billing
const table = new dynamodb.Table(this, 'OrdersTable', {
tableName: 'orders',
partitionKey: { name: 'pk', type: dynamodb.AttributeType.STRING },
sortKey: { name: 'sk', type: dynamodb.AttributeType.STRING },
// Billing mode: PAY_PER_REQUEST (on-demand) or PROVISIONED
billingMode: dynamodb.BillingMode.PAY_PER_REQUEST,
// Point-in-time recovery
pointInTimeRecovery: true,
// Encryption
encryption: dynamodb.TableEncryption.AWS_MANAGED,
// Streams for real-time processing
stream: dynamodb.StreamViewType.NEW_AND_OLD_IMAGES,
// TTL for automatic item expiration
timeToLiveAttribute: 'ttl',
removalPolicy: cdk.RemovalPolicy.RETAIN,
});
// Global Secondary Index
table.addGlobalSecondaryIndex({
indexName: 'gsi-status',
partitionKey: { name: 'status', type: dynamodb.AttributeType.STRING },
sortKey: { name: 'createdAt', type: dynamodb.AttributeType.STRING },
projectionType: dynamodb.ProjectionType.INCLUDE,
nonKeyAttributes: ['orderId', 'customerId', 'total'],
});
// Local Secondary Index
table.addLocalSecondaryIndex({
indexName: 'lsi-amount',
sortKey: { name: 'amount', type: dynamodb.AttributeType.NUMBER },
projectionType: dynamodb.ProjectionType.ALL,
});
}
}- Design for access patterns first, not data normalization
- Use composite keys (pk + sk) for one-to-many relationships
- Enable on-demand for unpredictable workloads
- Use DAX for microsecond read latency (read-heavy)
- Implement single-table design for related entities
Amazon Aurora
Aurora is AWS’s cloud-native relational database, 5x faster than MySQL and 3x faster than PostgreSQL. Aurora Serverless v2 scales automatically from 0.5 to 128 ACUs.
# Terraform: Aurora Serverless v2 PostgreSQL
resource "aws_rds_cluster" "aurora" {
cluster_identifier = "app-aurora"
engine = "aurora-postgresql"
engine_mode = "provisioned"
engine_version = "15.4"
database_name = "appdb"
master_username = "dbadmin"
master_password = var.db_password
db_subnet_group_name = aws_db_subnet_group.aurora.name
vpc_security_group_ids = [aws_security_group.aurora.id]
# Serverless v2 scaling
serverlessv2_scaling_configuration {
min_capacity = 0.5
max_capacity = 16
}
# Storage encryption
storage_encrypted = true
kms_key_id = aws_kms_key.rds.arn
# Backup
backup_retention_period = 30
preferred_backup_window = "03:00-04:00"
# Protection
deletion_protection = true
skip_final_snapshot = false
final_snapshot_identifier = "app-aurora-final"
}
resource "aws_rds_cluster_instance" "aurora" {
count = 2
identifier = "app-aurora-${count.index}"
cluster_identifier = aws_rds_cluster.aurora.id
instance_class = "db.serverless" # Serverless v2
engine = aws_rds_cluster.aurora.engine
engine_version = aws_rds_cluster.aurora.engine_version
performance_insights_enabled = true
}Database Selection Guide
| Requirement | Recommended Service | Why |
|---|---|---|
| Traditional RDBMS, complex joins | RDS (PostgreSQL/MySQL) | Full SQL, ACID transactions |
| High-performance RDBMS | Aurora | 5x MySQL performance, auto-scaling |
| Key-value, high throughput | DynamoDB | Single-digit ms, unlimited scale |
| Session/caching | ElastiCache (Redis) | Sub-millisecond latency |
| MongoDB compatibility | DocumentDB | Managed MongoDB API |
| Graph relationships | Neptune | Social networks, fraud detection |
Key Takeaways
- ✅ S3 for everything – Default storage for logs, backups, data lakes, static assets
- ✅ Use lifecycle policies – Automatically transition to cheaper storage classes
- ✅ Aurora > RDS – Choose Aurora for new workloads (better performance, same price)
- ✅ DynamoDB for scale – When you need predictable performance at any scale
- ✅ Enable encryption – All storage and databases should be encrypted at rest
- ✅ Multi-AZ for production – Always for RDS/Aurora production workloads
Conclusion
AWS storage and database services provide options for every workload pattern. Use S3 for object storage with intelligent lifecycle management, RDS/Aurora for relational workloads, and DynamoDB for high-throughput NoSQL. In Part 4, we’ll explore AWS networking including VPC, Route 53, and CloudFront.
References
Discover more from C4: Container, Code, Cloud & Context
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.