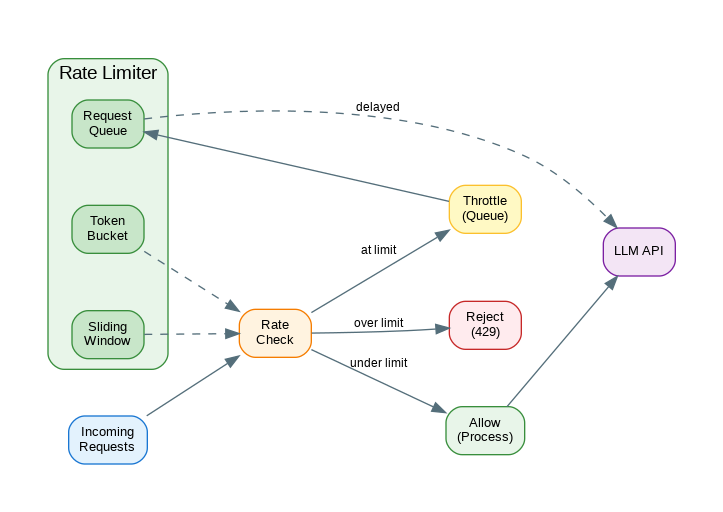
Introduction: LLM APIs have strict rate limits—requests per minute, tokens per minute, and concurrent request limits. Exceeding these limits results in 429 errors that can cascade through your application. Effective rate limiting on your side prevents hitting API limits, provides fair access across users, and enables graceful degradation under load. This guide covers practical rate limiting patterns: token bucket algorithms, sliding window counters, request queuing, and adaptive throttling that responds to API feedback.
Token Bucket Algorithm
import time
import asyncio
from threading import Lock
from dataclasses import dataclass
@dataclass
class TokenBucketConfig:
"""Configuration for token bucket."""
capacity: int # Maximum tokens
refill_rate: float # Tokens per second
initial_tokens: int = None # Starting tokens (defaults to capacity)
class TokenBucket:
"""Token bucket rate limiter."""
def __init__(self, config: TokenBucketConfig):
self.capacity = config.capacity
self.refill_rate = config.refill_rate
self.tokens = config.initial_tokens or config.capacity
self.last_refill = time.time()
self.lock = Lock()
def _refill(self):
"""Refill tokens based on elapsed time."""
now = time.time()
elapsed = now - self.last_refill
new_tokens = elapsed * self.refill_rate
self.tokens = min(self.capacity, self.tokens + new_tokens)
self.last_refill = now
def acquire(self, tokens: int = 1) -> bool:
"""Try to acquire tokens. Returns True if successful."""
with self.lock:
self._refill()
if self.tokens >= tokens:
self.tokens -= tokens
return True
return False
def wait_for_tokens(self, tokens: int = 1) -> float:
"""Calculate wait time for tokens to become available."""
with self.lock:
self._refill()
if self.tokens >= tokens:
return 0
needed = tokens - self.tokens
return needed / self.refill_rate
async def acquire_async(self, tokens: int = 1) -> bool:
"""Async acquire with waiting."""
wait_time = self.wait_for_tokens(tokens)
if wait_time > 0:
await asyncio.sleep(wait_time)
return self.acquire(tokens)
# LLM-specific rate limiter
class LLMRateLimiter:
"""Rate limiter for LLM APIs with RPM and TPM limits."""
def __init__(
self,
requests_per_minute: int = 60,
tokens_per_minute: int = 100000
):
# Request rate limiter
self.request_bucket = TokenBucket(TokenBucketConfig(
capacity=requests_per_minute,
refill_rate=requests_per_minute / 60
))
# Token rate limiter
self.token_bucket = TokenBucket(TokenBucketConfig(
capacity=tokens_per_minute,
refill_rate=tokens_per_minute / 60
))
def can_make_request(self, estimated_tokens: int = 1000) -> bool:
"""Check if request can be made."""
return (
self.request_bucket.acquire(1) and
self.token_bucket.acquire(estimated_tokens)
)
async def wait_for_capacity(self, estimated_tokens: int = 1000):
"""Wait until capacity is available."""
request_wait = self.request_bucket.wait_for_tokens(1)
token_wait = self.token_bucket.wait_for_tokens(estimated_tokens)
wait_time = max(request_wait, token_wait)
if wait_time > 0:
await asyncio.sleep(wait_time)
self.request_bucket.acquire(1)
self.token_bucket.acquire(estimated_tokens)
def record_actual_tokens(self, actual_tokens: int, estimated_tokens: int):
"""Adjust for actual token usage."""
diff = actual_tokens - estimated_tokens
if diff > 0:
# Used more than estimated, deduct extra
self.token_bucket.acquire(diff)
elif diff < 0:
# Used less, return tokens (up to capacity)
with self.token_bucket.lock:
self.token_bucket.tokens = min(
self.token_bucket.capacity,
self.token_bucket.tokens - diff
)
# Usage
limiter = LLMRateLimiter(
requests_per_minute=60,
tokens_per_minute=100000
)
async def rate_limited_completion(prompt: str) -> str:
"""Make rate-limited LLM call."""
estimated_tokens = len(prompt.split()) * 2 # Rough estimate
await limiter.wait_for_capacity(estimated_tokens)
from openai import OpenAI
client = OpenAI()
response = client.chat.completions.create(
model="gpt-4o-mini",
messages=[{"role": "user", "content": prompt}]
)
actual_tokens = response.usage.total_tokens
limiter.record_actual_tokens(actual_tokens, estimated_tokens)
return response.choices[0].message.contentSliding Window Rate Limiter
from collections import deque
from dataclasses import dataclass
import time
@dataclass
class SlidingWindowConfig:
"""Configuration for sliding window."""
window_size: float # Window size in seconds
max_requests: int # Maximum requests in window
class SlidingWindowLimiter:
"""Sliding window rate limiter."""
def __init__(self, config: SlidingWindowConfig):
self.window_size = config.window_size
self.max_requests = config.max_requests
self.requests: deque = deque()
self.lock = Lock()
def _cleanup(self):
"""Remove expired requests from window."""
cutoff = time.time() - self.window_size
while self.requests and self.requests[0] < cutoff:
self.requests.popleft()
def acquire(self) -> bool:
"""Try to acquire a slot in the window."""
with self.lock:
self._cleanup()
if len(self.requests) < self.max_requests:
self.requests.append(time.time())
return True
return False
def wait_time(self) -> float:
"""Calculate time until a slot is available."""
with self.lock:
self._cleanup()
if len(self.requests) < self.max_requests:
return 0
# Wait until oldest request expires
oldest = self.requests[0]
return (oldest + self.window_size) - time.time()
def get_remaining(self) -> int:
"""Get remaining requests in current window."""
with self.lock:
self._cleanup()
return self.max_requests - len(self.requests)
class SlidingWindowCounter:
"""Sliding window counter with sub-window precision."""
def __init__(
self,
window_size: float,
max_count: int,
precision: int = 10
):
self.window_size = window_size
self.max_count = max_count
self.precision = precision
self.sub_window = window_size / precision
self.counts: dict[int, int] = {}
self.lock = Lock()
def _get_window_key(self, timestamp: float) -> int:
"""Get sub-window key for timestamp."""
return int(timestamp / self.sub_window)
def _cleanup(self, current_key: int):
"""Remove old sub-windows."""
cutoff = current_key - self.precision
keys_to_remove = [k for k in self.counts if k < cutoff]
for k in keys_to_remove:
del self.counts[k]
def _get_count(self, current_key: int) -> float:
"""Get weighted count across window."""
total = 0
current_time = time.time()
window_start = current_time - self.window_size
for key, count in self.counts.items():
sub_window_start = key * self.sub_window
sub_window_end = sub_window_start + self.sub_window
if sub_window_end <= window_start:
continue
if sub_window_start >= current_time:
continue
# Calculate overlap weight
overlap_start = max(sub_window_start, window_start)
overlap_end = min(sub_window_end, current_time)
weight = (overlap_end - overlap_start) / self.sub_window
total += count * weight
return total
def acquire(self, count: int = 1) -> bool:
"""Try to acquire count."""
with self.lock:
current_key = self._get_window_key(time.time())
self._cleanup(current_key)
current_count = self._get_count(current_key)
if current_count + count <= self.max_count:
self.counts[current_key] = self.counts.get(current_key, 0) + count
return True
return False
# Per-user rate limiting
class UserRateLimiter:
"""Rate limiter with per-user limits."""
def __init__(
self,
requests_per_minute: int = 10,
tokens_per_minute: int = 10000
):
self.rpm = requests_per_minute
self.tpm = tokens_per_minute
self.user_limiters: dict[str, LLMRateLimiter] = {}
self.lock = Lock()
def get_limiter(self, user_id: str) -> LLMRateLimiter:
"""Get or create limiter for user."""
with self.lock:
if user_id not in self.user_limiters:
self.user_limiters[user_id] = LLMRateLimiter(
requests_per_minute=self.rpm,
tokens_per_minute=self.tpm
)
return self.user_limiters[user_id]
async def acquire_for_user(
self,
user_id: str,
estimated_tokens: int = 1000
):
"""Acquire rate limit for user."""
limiter = self.get_limiter(user_id)
await limiter.wait_for_capacity(estimated_tokens)Request Queue
import asyncio
from dataclasses import dataclass, field
from typing import Callable, Any
from enum import Enum
import heapq
class Priority(int, Enum):
HIGH = 1
NORMAL = 2
LOW = 3
@dataclass(order=True)
class QueuedRequest:
"""A request in the queue."""
priority: int
timestamp: float = field(compare=False)
request_id: str = field(compare=False)
callback: Callable = field(compare=False)
args: tuple = field(compare=False, default=())
kwargs: dict = field(compare=False, default_factory=dict)
future: asyncio.Future = field(compare=False, default=None)
class RequestQueue:
"""Priority queue for LLM requests."""
def __init__(
self,
max_concurrent: int = 5,
max_queue_size: int = 100
):
self.max_concurrent = max_concurrent
self.max_queue_size = max_queue_size
self.queue: list[QueuedRequest] = []
self.active_count = 0
self.lock = asyncio.Lock()
self.processing = False
async def enqueue(
self,
callback: Callable,
*args,
priority: Priority = Priority.NORMAL,
**kwargs
) -> Any:
"""Add request to queue and wait for result."""
async with self.lock:
if len(self.queue) >= self.max_queue_size:
raise QueueFullError("Request queue is full")
future = asyncio.Future()
request = QueuedRequest(
priority=priority.value,
timestamp=time.time(),
request_id=str(uuid.uuid4()),
callback=callback,
args=args,
kwargs=kwargs,
future=future
)
heapq.heappush(self.queue, request)
# Start processing if not already running
if not self.processing:
asyncio.create_task(self._process_queue())
return await future
async def _process_queue(self):
"""Process requests from queue."""
self.processing = True
while True:
async with self.lock:
if not self.queue:
self.processing = False
return
if self.active_count >= self.max_concurrent:
# Wait for a slot
pass
else:
request = heapq.heappop(self.queue)
self.active_count += 1
asyncio.create_task(self._execute_request(request))
await asyncio.sleep(0.01)
async def _execute_request(self, request: QueuedRequest):
"""Execute a single request."""
try:
if asyncio.iscoroutinefunction(request.callback):
result = await request.callback(*request.args, **request.kwargs)
else:
result = request.callback(*request.args, **request.kwargs)
request.future.set_result(result)
except Exception as e:
request.future.set_exception(e)
finally:
async with self.lock:
self.active_count -= 1
class QueueFullError(Exception):
pass
# Adaptive queue with backpressure
class AdaptiveQueue:
"""Queue that adapts to API response times."""
def __init__(
self,
initial_concurrent: int = 5,
min_concurrent: int = 1,
max_concurrent: int = 20
):
self.concurrent = initial_concurrent
self.min_concurrent = min_concurrent
self.max_concurrent = max_concurrent
self.queue = RequestQueue(max_concurrent=self.concurrent)
self.latencies: deque = deque(maxlen=100)
self.errors: deque = deque(maxlen=100)
def record_latency(self, latency_ms: float):
"""Record request latency."""
self.latencies.append(latency_ms)
self._adjust_concurrency()
def record_error(self, is_rate_limit: bool):
"""Record error."""
self.errors.append({"rate_limit": is_rate_limit, "time": time.time()})
if is_rate_limit:
self._decrease_concurrency()
def _adjust_concurrency(self):
"""Adjust concurrency based on performance."""
if len(self.latencies) < 10:
return
avg_latency = sum(self.latencies) / len(self.latencies)
# Recent rate limit errors
recent_errors = [
e for e in self.errors
if e["rate_limit"] and time.time() - e["time"] < 60
]
if len(recent_errors) > 3:
self._decrease_concurrency()
elif avg_latency < 500 and len(recent_errors) == 0:
self._increase_concurrency()
def _increase_concurrency(self):
"""Increase concurrent requests."""
if self.concurrent < self.max_concurrent:
self.concurrent = min(self.concurrent + 1, self.max_concurrent)
self.queue.max_concurrent = self.concurrent
def _decrease_concurrency(self):
"""Decrease concurrent requests."""
if self.concurrent > self.min_concurrent:
self.concurrent = max(self.concurrent - 2, self.min_concurrent)
self.queue.max_concurrent = self.concurrentAdaptive Throttling
from dataclasses import dataclass
from typing import Optional
@dataclass
class ThrottleState:
"""Current throttle state."""
requests_per_second: float
last_429_time: Optional[float] = None
consecutive_429s: int = 0
backoff_until: Optional[float] = None
class AdaptiveThrottler:
"""Throttler that adapts to API feedback."""
def __init__(
self,
initial_rps: float = 1.0,
min_rps: float = 0.1,
max_rps: float = 10.0,
backoff_factor: float = 0.5,
recovery_factor: float = 1.1
):
self.state = ThrottleState(requests_per_second=initial_rps)
self.min_rps = min_rps
self.max_rps = max_rps
self.backoff_factor = backoff_factor
self.recovery_factor = recovery_factor
self.last_request_time = 0
self.lock = Lock()
def _get_delay(self) -> float:
"""Calculate delay between requests."""
return 1.0 / self.state.requests_per_second
async def acquire(self):
"""Wait for throttle and acquire permission."""
with self.lock:
# Check if in backoff
if self.state.backoff_until:
if time.time() < self.state.backoff_until:
wait_time = self.state.backoff_until - time.time()
await asyncio.sleep(wait_time)
self.state.backoff_until = None
# Calculate wait time
elapsed = time.time() - self.last_request_time
delay = self._get_delay()
if elapsed < delay:
await asyncio.sleep(delay - elapsed)
self.last_request_time = time.time()
def record_success(self):
"""Record successful request."""
with self.lock:
self.state.consecutive_429s = 0
# Gradually increase rate
if time.time() - (self.state.last_429_time or 0) > 60:
self.state.requests_per_second = min(
self.state.requests_per_second * self.recovery_factor,
self.max_rps
)
def record_rate_limit(self, retry_after: float = None):
"""Record rate limit error."""
with self.lock:
self.state.last_429_time = time.time()
self.state.consecutive_429s += 1
# Decrease rate
self.state.requests_per_second = max(
self.state.requests_per_second * self.backoff_factor,
self.min_rps
)
# Set backoff
if retry_after:
self.state.backoff_until = time.time() + retry_after
else:
# Exponential backoff based on consecutive errors
backoff = min(60, 2 ** self.state.consecutive_429s)
self.state.backoff_until = time.time() + backoff
# Combined rate limiter with adaptive throttling
class SmartRateLimiter:
"""Combines multiple rate limiting strategies."""
def __init__(
self,
rpm: int = 60,
tpm: int = 100000
):
self.token_limiter = LLMRateLimiter(rpm, tpm)
self.throttler = AdaptiveThrottler(initial_rps=rpm / 60)
self.queue = AdaptiveQueue()
async def execute(
self,
func: Callable,
*args,
estimated_tokens: int = 1000,
priority: Priority = Priority.NORMAL,
**kwargs
) -> Any:
"""Execute function with rate limiting."""
async def wrapped():
# Wait for throttle
await self.throttler.acquire()
# Wait for token capacity
await self.token_limiter.wait_for_capacity(estimated_tokens)
try:
start = time.time()
result = await func(*args, **kwargs)
latency = (time.time() - start) * 1000
self.throttler.record_success()
self.queue.record_latency(latency)
return result
except Exception as e:
if "429" in str(e) or "rate" in str(e).lower():
retry_after = getattr(e, "retry_after", None)
self.throttler.record_rate_limit(retry_after)
self.queue.record_error(is_rate_limit=True)
else:
self.queue.record_error(is_rate_limit=False)
raise
return await self.queue.enqueue(wrapped, priority=priority)Production Rate Limiting Service
from fastapi import FastAPI, HTTPException, Request, Depends
from fastapi.responses import JSONResponse
from pydantic import BaseModel
app = FastAPI()
# Initialize rate limiters
global_limiter = SmartRateLimiter(rpm=500, tpm=1000000)
user_limiter = UserRateLimiter(requests_per_minute=20, tokens_per_minute=50000)
class CompletionRequest(BaseModel):
prompt: str
priority: str = "normal"
async def get_user_id(request: Request) -> str:
"""Extract user ID from request."""
# From header, token, or session
user_id = request.headers.get("X-User-ID", "anonymous")
return user_id
@app.post("/complete")
async def complete(
request: CompletionRequest,
user_id: str = Depends(get_user_id)
):
"""Rate-limited completion endpoint."""
# Estimate tokens
estimated_tokens = len(request.prompt.split()) * 2
# Check user rate limit
user_rate_limiter = user_limiter.get_limiter(user_id)
if not user_rate_limiter.can_make_request(estimated_tokens):
raise HTTPException(
status_code=429,
detail="User rate limit exceeded",
headers={"Retry-After": "60"}
)
# Map priority
priority_map = {
"high": Priority.HIGH,
"normal": Priority.NORMAL,
"low": Priority.LOW
}
priority = priority_map.get(request.priority, Priority.NORMAL)
try:
async def call_llm():
from openai import OpenAI
client = OpenAI()
response = client.chat.completions.create(
model="gpt-4o-mini",
messages=[{"role": "user", "content": request.prompt}]
)
return response
response = await global_limiter.execute(
call_llm,
estimated_tokens=estimated_tokens,
priority=priority
)
# Record actual usage
actual_tokens = response.usage.total_tokens
user_rate_limiter.record_actual_tokens(actual_tokens, estimated_tokens)
return {
"response": response.choices[0].message.content,
"tokens_used": actual_tokens
}
except Exception as e:
if "429" in str(e):
raise HTTPException(
status_code=429,
detail="API rate limit exceeded. Please try again later.",
headers={"Retry-After": "30"}
)
raise
@app.get("/rate-limit/status")
async def rate_limit_status(user_id: str = Depends(get_user_id)):
"""Get rate limit status for user."""
limiter = user_limiter.get_limiter(user_id)
return {
"user_id": user_id,
"requests_remaining": limiter.request_bucket.tokens,
"tokens_remaining": limiter.token_bucket.tokens,
"throttle_rps": global_limiter.throttler.state.requests_per_second
}
# Rate limit exceeded handler
@app.exception_handler(429)
async def rate_limit_handler(request: Request, exc: HTTPException):
return JSONResponse(
status_code=429,
content={
"error": "rate_limit_exceeded",
"message": exc.detail,
"retry_after": exc.headers.get("Retry-After", "60")
},
headers=exc.headers
)References
- OpenAI Rate Limits: https://platform.openai.com/docs/guides/rate-limits
- Token Bucket Algorithm: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Token_bucket
- Sliding Window Counter: https://blog.cloudflare.com/counting-things-a-lot-of-different-things/
- Anthropic Rate Limits: https://docs.anthropic.com/en/api/rate-limits
Conclusion
Effective rate limiting is essential for production LLM applications. Use token bucket algorithms for smooth rate limiting that allows bursts while maintaining average rates. Implement sliding window counters for precise per-user limits. Queue requests with priorities to ensure important requests get processed first during high load. Adaptive throttling responds to API feedback—backing off on 429 errors and gradually recovering. Combine these strategies: global limits protect your API quota, per-user limits ensure fair access, and adaptive throttling optimizes throughput. Monitor your rate limit metrics and adjust limits based on actual usage patterns and API tier.
Discover more from C4: Container, Code, Cloud & Context
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.