The modern enterprise data landscape demands more than traditional data warehousing or isolated analytics solutions. Organizations need unified platforms that can handle everything from batch ETL processing to real-time streaming analytics, from structured data warehousing to exploratory data science workloads. Azure Synapse Analytics represents Microsoft’s answer to this challenge—a comprehensive analytics service that brings together data integration, enterprise data warehousing, and big data analytics under a single unified experience. Having architected numerous data platforms across industries, I’ve found that understanding Synapse’s architectural nuances is essential for building solutions that truly deliver on the promise of unified analytics.
The Unified Analytics Vision
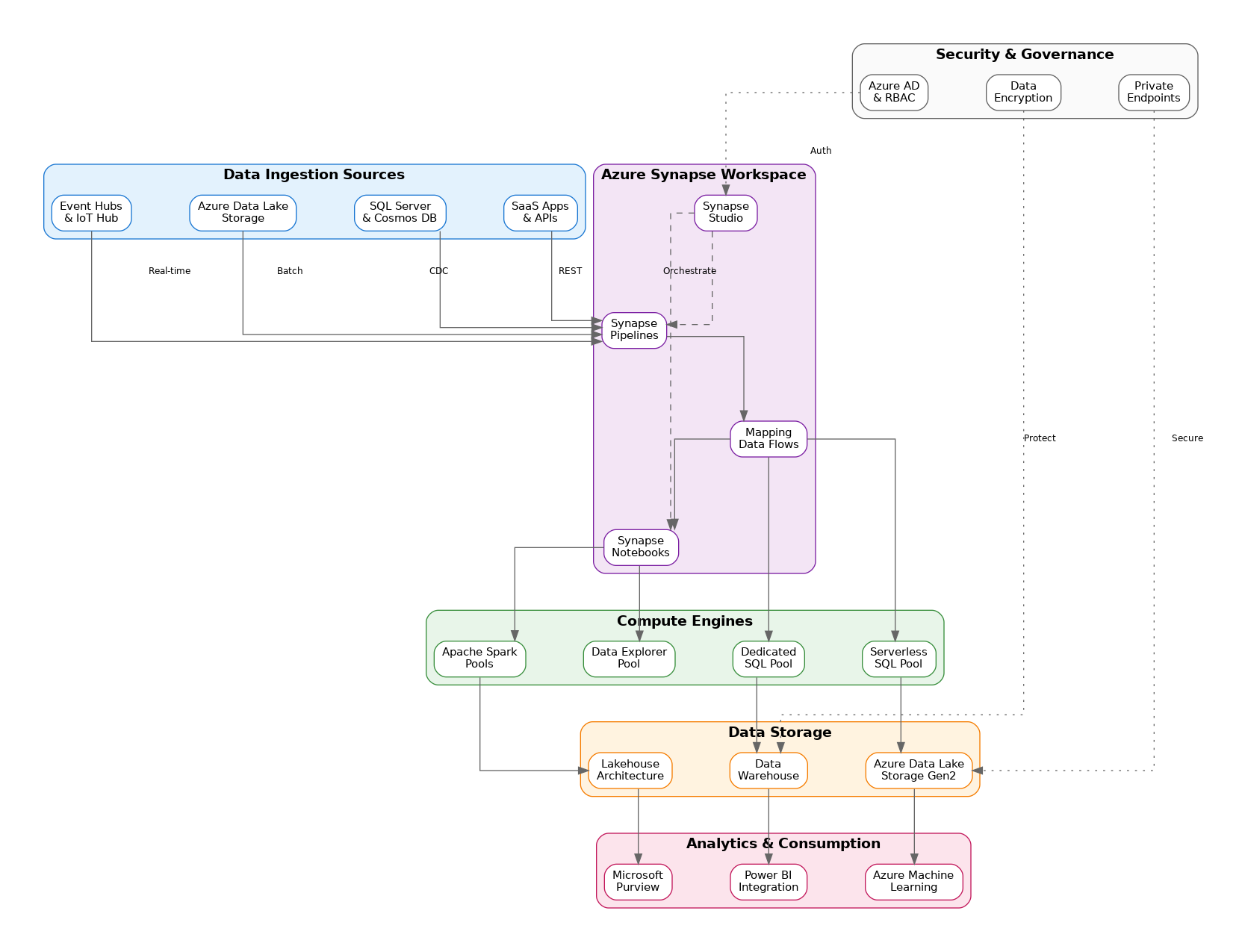
Azure Synapse Analytics emerged from the evolution of Azure SQL Data Warehouse, but it represents far more than a rebranding exercise. The platform integrates multiple compute engines—dedicated SQL pools for enterprise data warehousing, serverless SQL pools for ad-hoc querying, Apache Spark pools for big data processing, and Data Explorer pools for log and telemetry analytics. This multi-engine approach allows organizations to choose the right tool for each workload without managing separate platforms or dealing with data silos.
Synapse Workspace: The Unified Experience
Synapse Studio provides a unified development experience that brings together data engineers, data scientists, and business analysts. The workspace concept centralizes management of compute resources, data connections, and development artifacts. Unlike traditional approaches where teams work in isolated tools, Synapse Studio enables collaboration through shared notebooks, SQL scripts, and data pipelines—all version-controlled through Git integration.
The linked services architecture abstracts connection management from development artifacts. Data engineers define connections to source systems once, and those connections become available across pipelines, notebooks, and SQL scripts. This separation of concerns simplifies credential management and enables environment-specific configurations without modifying code.
Dedicated SQL Pools: Enterprise Data Warehousing
Dedicated SQL pools provide massively parallel processing (MPP) architecture for enterprise data warehousing workloads. The distributed query engine partitions data across compute nodes, enabling sub-second query performance on petabyte-scale datasets. Understanding distribution strategies—hash, round-robin, and replicated—proves essential for optimizing query performance and minimizing data movement during joins.
Workload management capabilities enable resource governance across concurrent users and workloads. Workload groups define resource allocation policies, while workload classifiers route queries to appropriate groups based on user identity, query characteristics, or explicit labels. This fine-grained control prevents runaway queries from impacting critical business reporting.
Serverless SQL Pools: On-Demand Analytics
Serverless SQL pools enable querying data directly in Azure Data Lake Storage without loading it into dedicated storage. This capability transforms how organizations approach exploratory analytics and data discovery. Analysts can query Parquet, CSV, or JSON files using familiar T-SQL syntax, paying only for the data processed rather than provisioned capacity.
The logical data warehouse pattern leverages serverless SQL pools to create virtualized views over data lake files. External tables and views provide a SQL interface to raw data, enabling self-service analytics without the latency and cost of traditional ETL loading. This approach proves particularly valuable for data that’s queried infrequently or where freshness requirements preclude batch loading.
Apache Spark Pools: Big Data Processing
Spark pools bring Apache Spark’s distributed processing capabilities into the Synapse ecosystem. Data engineers can develop transformations in Python, Scala, or .NET, leveraging Spark’s rich ecosystem of libraries for machine learning, graph processing, and streaming analytics. The managed Spark experience handles cluster provisioning, scaling, and optimization automatically.
Notebook-based development enables interactive data exploration and iterative algorithm development. Data scientists can prototype transformations, visualize results, and collaborate with colleagues—all within Synapse Studio. The integration with MLflow provides experiment tracking and model registry capabilities, bridging the gap between experimentation and production deployment.
Synapse Pipelines: Data Integration
Synapse Pipelines inherit Azure Data Factory’s proven data integration capabilities while adding tight integration with Synapse compute resources. The visual pipeline designer enables no-code data movement and transformation, while code-first approaches support complex orchestration scenarios. Mapping data flows provide visual ETL with Spark-based execution, democratizing complex transformations for business users.
The integration runtime architecture supports hybrid scenarios spanning cloud and on-premises data sources. Self-hosted integration runtimes bridge corporate firewalls, enabling secure data movement without exposing internal systems to the internet. This flexibility proves essential for enterprises with significant on-premises data investments.
Data Lake Integration
Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2 serves as the foundation for Synapse’s lakehouse architecture. The hierarchical namespace provides file system semantics with object storage economics, while ABFS driver integration enables high-performance access from all Synapse compute engines. Understanding storage organization—bronze, silver, gold layers—helps establish data governance patterns that scale with organizational growth.
Delta Lake format support brings ACID transactions to data lake storage. Data engineers can perform upserts, deletes, and time-travel queries on lake data, capabilities previously limited to traditional databases. This convergence of data lake flexibility with database reliability enables the lakehouse architecture that many organizations aspire to implement.
Security and Governance
Synapse implements defense-in-depth security through multiple layers. Managed virtual networks isolate Synapse workspaces from public internet, while private endpoints provide secure connectivity to data sources. Azure Active Directory integration enables single sign-on and role-based access control, while column-level and row-level security protect sensitive data within SQL pools.
Microsoft Purview integration extends governance capabilities beyond Synapse boundaries. Automated data discovery catalogs assets across the data estate, while lineage tracking captures data flow from source systems through transformations to consumption. This visibility proves invaluable for compliance requirements and impact analysis when source systems change.
Performance Optimization
Optimizing Synapse performance requires understanding each compute engine’s characteristics. Dedicated SQL pools benefit from proper distribution key selection, materialized views, and result set caching. Serverless SQL pools perform best with properly partitioned Parquet files and selective column projection. Spark pools require attention to cluster sizing, partition strategies, and broadcast join thresholds.
Monitoring and diagnostics capabilities help identify performance bottlenecks. Query Store captures execution plans and runtime statistics for dedicated SQL pools, while Spark UI provides detailed job and stage metrics. Azure Monitor integration enables alerting on resource utilization and query performance degradation.
Cost Management
Synapse pricing varies significantly across compute engines. Dedicated SQL pools charge for provisioned capacity regardless of utilization, making them cost-effective for predictable, sustained workloads. Serverless SQL pools charge per terabyte processed, ideal for sporadic or exploratory queries. Spark pools charge for compute time, with auto-pause capabilities reducing costs during idle periods.
Reserved capacity pricing provides significant discounts for committed usage. Organizations with predictable dedicated SQL pool requirements can achieve 40-65% cost savings through one or three-year reservations. Combining reserved capacity for baseline workloads with serverless capabilities for variable demand optimizes overall cost efficiency.
Implementation Considerations
Successful Synapse implementations require careful planning across multiple dimensions. Data architecture decisions—lakehouse vs. traditional warehouse, real-time vs. batch processing—shape the entire solution. Security requirements influence network topology and access control patterns. Performance expectations drive compute engine selection and optimization strategies.
For solutions architects evaluating Azure Synapse Analytics, the platform offers compelling capabilities for organizations seeking unified analytics. The key lies in understanding which compute engines align with specific workload requirements and designing architectures that leverage each engine’s strengths while maintaining operational simplicity and cost efficiency.
Discover more from C4: Container, Code, Cloud & Context
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.