In the world of enterprise IT, data is the lifeblood of business operations. After two decades of architecting solutions across industries, I’ve witnessed firsthand how a robust backup strategy can mean the difference between business continuity and catastrophic data loss. Azure Backup has evolved into a comprehensive data protection platform that addresses the complex requirements of modern hybrid environments.
Understanding the Recovery Services Vault
At the heart of Azure Backup lies the Recovery Services Vault, a management entity that stores backup data and recovery points. Unlike traditional backup solutions that require dedicated infrastructure, the vault abstracts away the complexity of storage management while providing enterprise-grade durability. Each vault is geo-redundant by default, meaning your backup data is replicated across Azure regions, providing protection against regional outages.
The vault architecture supports multiple workload types simultaneously. You can protect Azure VMs, SQL databases, Azure Files, blob storage, on-premises servers via the MARS agent, and even SAP HANA workloads from a single management plane. This unified approach significantly reduces operational overhead compared to managing disparate backup solutions.


Storage Tiers and Cost Optimization
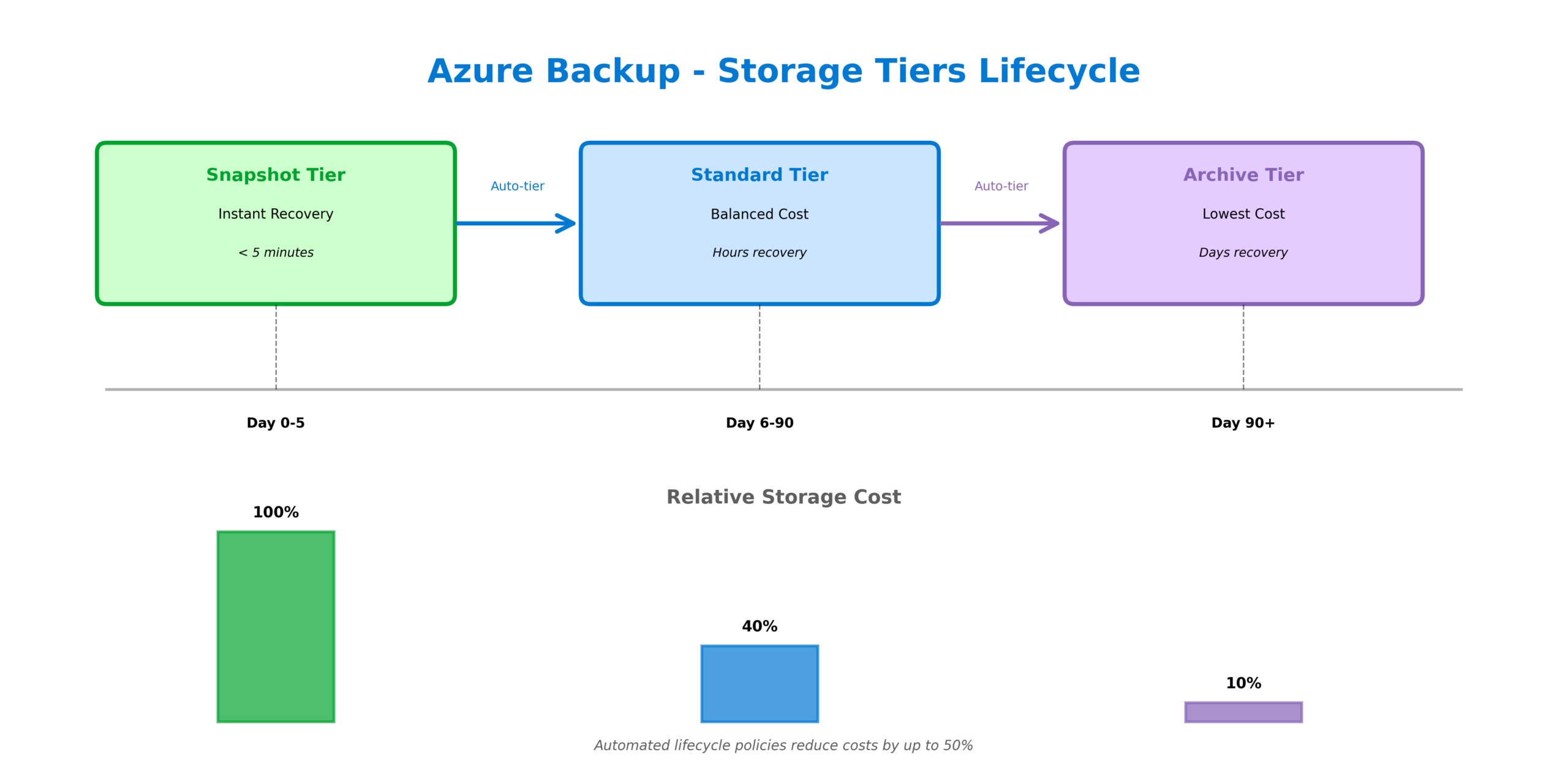
Azure Backup implements a tiered storage model that balances recovery speed with cost efficiency. The snapshot tier provides instant recovery capabilities, allowing you to restore VMs within minutes rather than hours. These snapshots are stored locally in your subscription for rapid access. The standard vault tier stores backup data in Azure-managed storage with configurable redundancy options. For long-term retention requirements, the archive tier offers significantly reduced storage costs for data that rarely needs to be accessed.
The intelligent tiering policies automatically move data between tiers based on your retention rules. For example, daily backups might remain in the standard tier for 30 days before being moved to archive storage for compliance retention. This automated lifecycle management can reduce backup storage costs by 50% or more compared to keeping all data in the standard tier.
Backup Policies and Scheduling
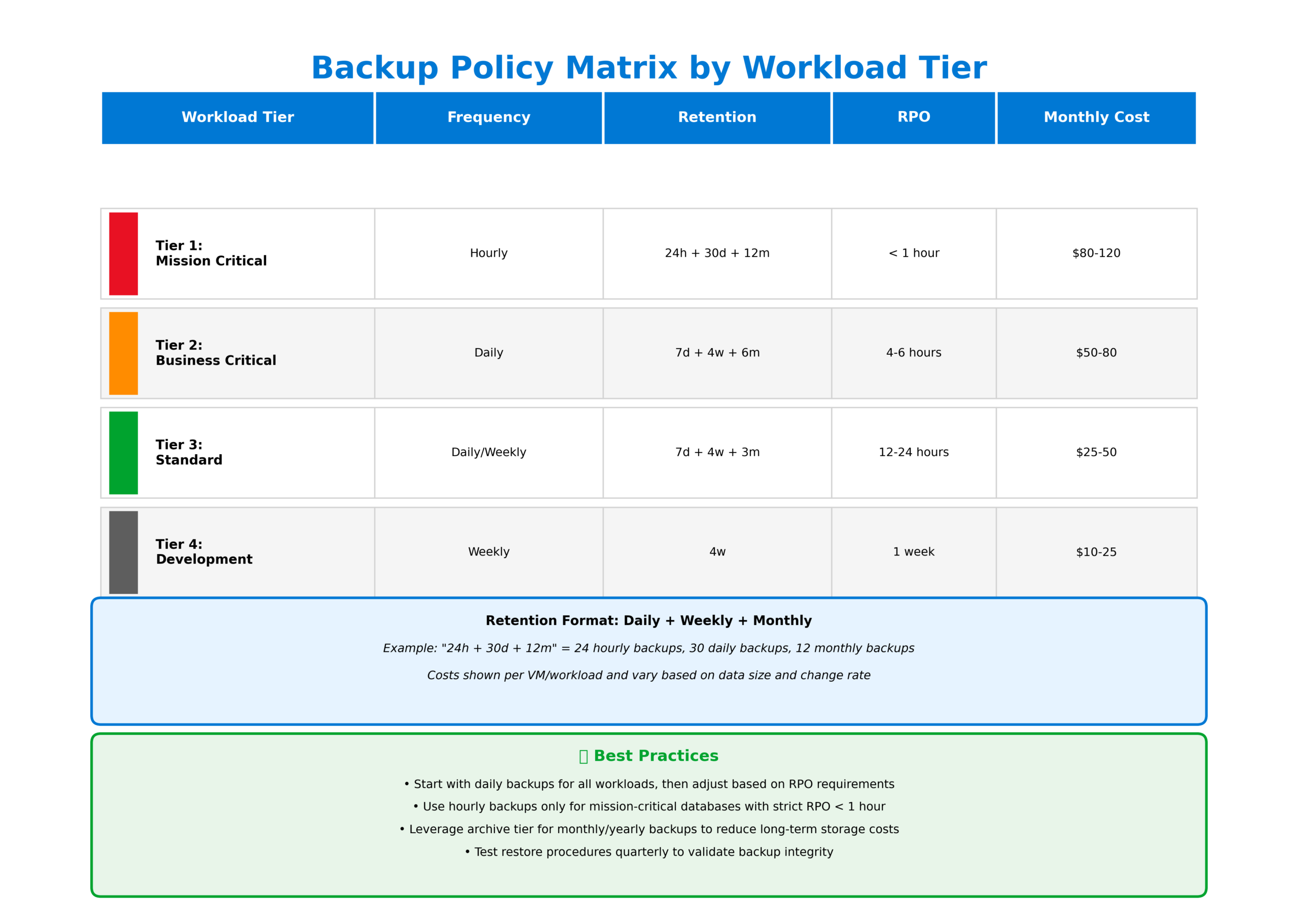
Effective backup strategies require granular control over scheduling and retention. Azure Backup policies support multiple backup frequencies including hourly, daily, weekly, monthly, and yearly schedules. The policy engine allows you to define different retention periods for each frequency, enabling compliance with regulatory requirements that mandate specific retention periods.
For critical workloads, I recommend implementing a tiered policy approach. Production databases might use hourly backups with 24-hour retention, daily backups retained for 30 days, weekly backups for 12 weeks, and monthly backups for 12 months. This approach provides multiple recovery points while optimizing storage consumption.
Recovery Options and Scenarios
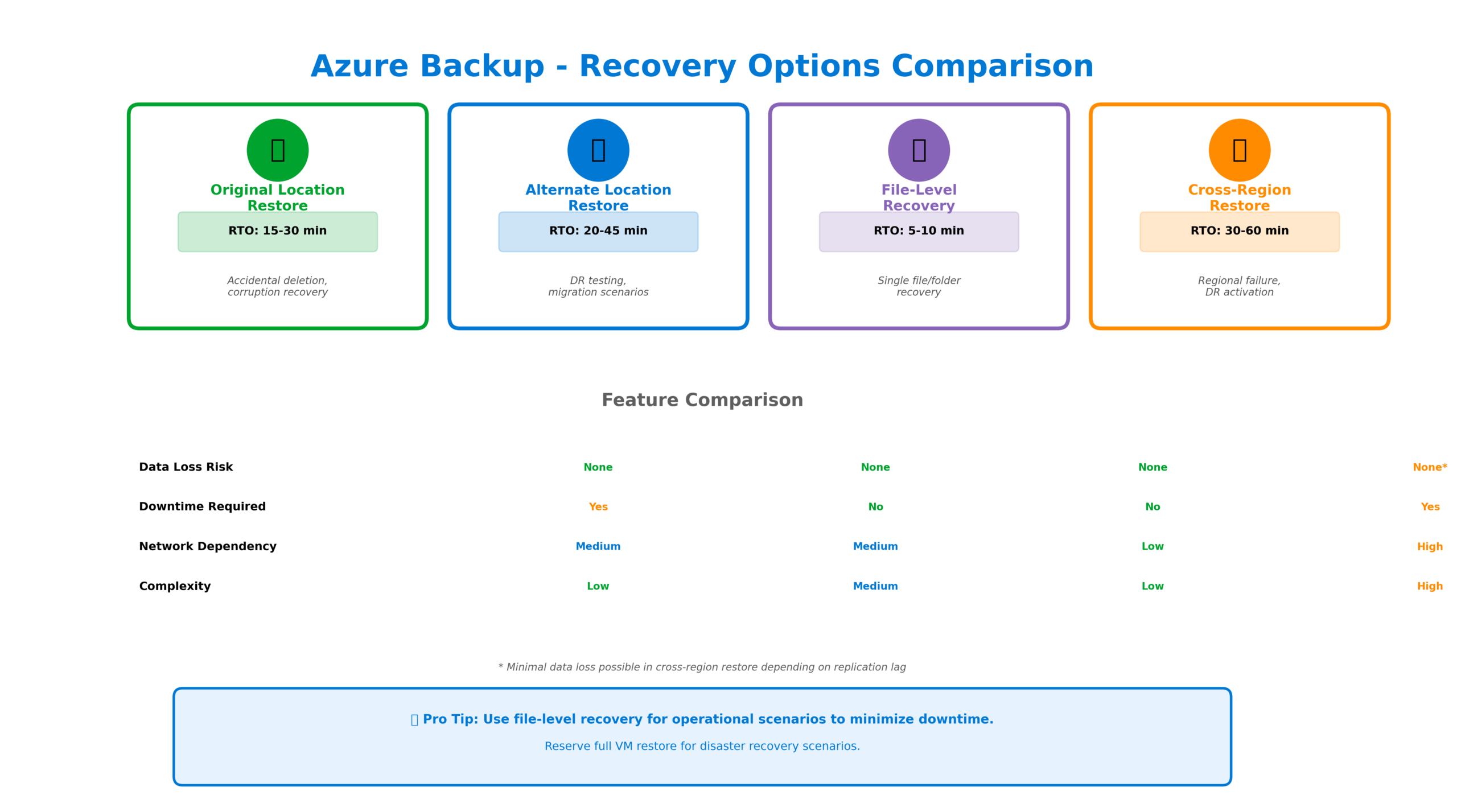
Azure Backup provides flexible recovery options to address various disaster scenarios. Original location restore returns data to its source, ideal for recovering from accidental deletion or corruption. Alternate location restore allows you to recover to a different VM, storage account, or even a different region, essential for disaster recovery testing and migration scenarios.
File-level recovery is particularly valuable for operational recovery scenarios. Rather than restoring an entire VM to recover a single file, you can mount the recovery point as a drive and browse to extract specific files. This capability dramatically reduces recovery time for common scenarios like accidentally deleted documents or corrupted application files.
Cross-Region Restore and Disaster Recovery
For organizations with stringent disaster recovery requirements, cross-region restore provides the ability to recover workloads in a secondary Azure region. When enabled, backup data is replicated to the paired region, allowing recovery even if the primary region experiences a complete outage. This capability is essential for meeting recovery point objectives (RPO) and recovery time objectives (RTO) defined in business continuity plans.
Security and Compliance
Azure Backup implements multiple security layers to protect backup data. Encryption at rest uses Azure-managed keys by default, with the option to bring your own keys stored in Azure Key Vault. Soft delete provides a 14-day recovery window for accidentally deleted backup data, protecting against both user error and ransomware attacks that target backup infrastructure.
Role-based access control (RBAC) enables granular permissions management. Backup operators can perform backup and restore operations without having access to the underlying data. Backup readers can monitor backup status without modification capabilities. This separation of duties is essential for maintaining security in enterprise environments.

When to Use What
Choosing the right backup approach depends on your specific requirements. For Azure VMs, use Azure Backup with application-consistent snapshots for databases and file-consistent snapshots for general workloads. For Azure SQL Database, leverage the built-in automated backups with point-in-time restore, supplementing with Azure Backup for long-term retention beyond 35 days.
For hybrid scenarios with on-premises servers, deploy the MARS agent for file and folder backup, or use Azure Backup Server for application-aware protection of SQL Server, Exchange, and SharePoint. For large-scale VM protection, consider Azure Site Recovery for disaster recovery with continuous replication, using Azure Backup for point-in-time recovery.
Implementation Best Practices
Start by defining your recovery objectives before implementing backup policies. Document RPO and RTO requirements for each workload class, then design policies that meet these objectives while optimizing costs. Implement backup monitoring through Azure Monitor and configure alerts for backup failures. Regularly test recovery procedures to validate that backups are actually recoverable.
Consider implementing backup governance through Azure Policy. Enforce backup requirements across subscriptions, ensuring that all VMs are protected and that backup policies meet organizational standards. Use tags to categorize workloads by criticality and apply appropriate backup policies automatically.
Looking Forward
Azure Backup continues to evolve with enhanced capabilities for modern workloads. Recent additions include support for Azure Kubernetes Service backup, improved integration with Azure Arc for hybrid scenarios, and enhanced ransomware protection features. As organizations increasingly adopt cloud-native architectures, backup strategies must evolve to protect containerized workloads, serverless functions, and distributed data stores.
The key to successful data protection lies in treating backup as a first-class architectural concern rather than an afterthought. By leveraging Azure Backup’s comprehensive capabilities and following enterprise best practices, organizations can build resilient systems that protect their most valuable asset: their data.
Discover more from C4: Container, Code, Cloud & Context
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.