Introduction: Ollama has revolutionized how developers run large language models locally. With a simple command-line interface and seamless hardware acceleration, you can have Llama 3.2, Mistral, or CodeLlama running on your laptop in minutes—no cloud API keys, no usage costs, complete privacy. Built on llama.cpp, Ollama abstracts away the complexity of model quantization, memory management, and GPU acceleration, making local AI accessible to everyone. This guide covers everything from installation to building production applications with Ollama.
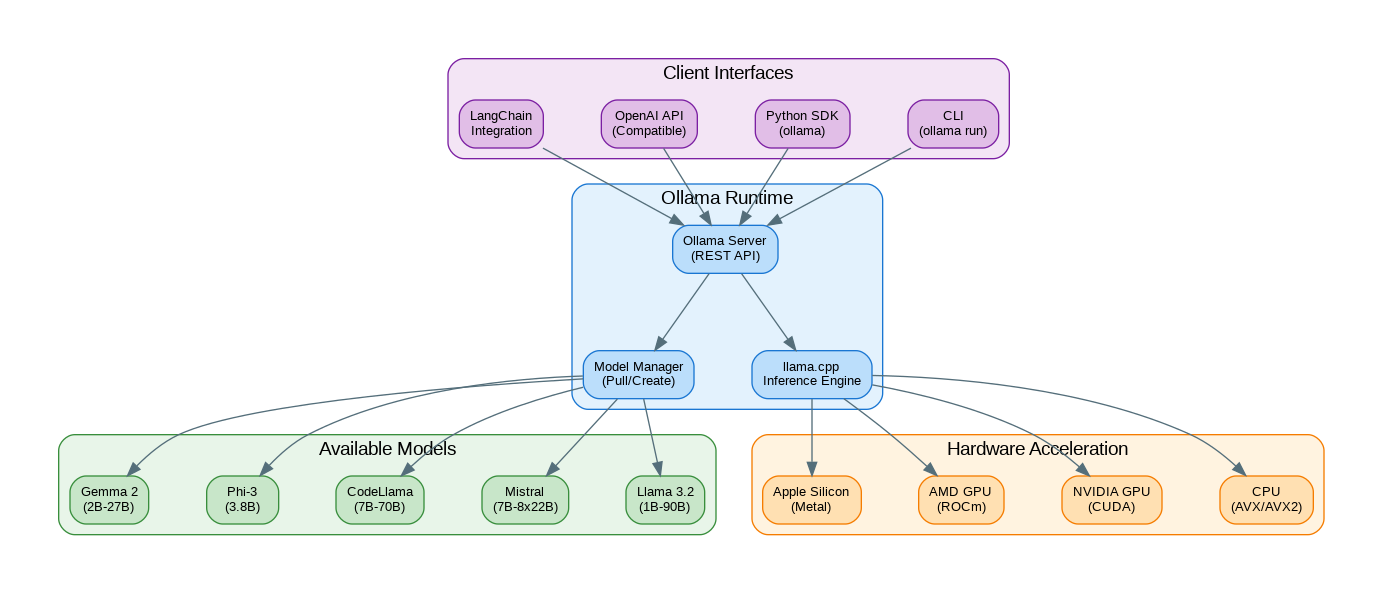
Getting Started with Ollama
# Installation
# macOS
brew install ollama
# Linux
curl -fsSL https://ollama.com/install.sh | sh
# Windows (download from ollama.com)
# Or use WSL2 with Linux installation
# Start the Ollama server (runs in background)
ollama serve
# Pull a model
ollama pull llama3.2 # Latest Llama 3.2 (3B default)
ollama pull llama3.2:1b # Smaller 1B version
ollama pull llama3.2:70b # Largest version (needs 48GB+ RAM)
ollama pull codellama # Code-specialized model
ollama pull mistral # Mistral 7B
ollama pull phi3 # Microsoft Phi-3
# Run interactive chat
ollama run llama3.2
# Run with a specific prompt
ollama run llama3.2 "Explain Docker in one paragraph"
# List downloaded models
ollama list
# Show model details
ollama show llama3.2
# Remove a model
ollama rm codellamaPython SDK Usage
import ollama
# Simple chat completion
response = ollama.chat(
model='llama3.2',
messages=[
{'role': 'system', 'content': 'You are a helpful coding assistant.'},
{'role': 'user', 'content': 'Write a Python function to reverse a string'}
]
)
print(response['message']['content'])
# Streaming responses
stream = ollama.chat(
model='llama3.2',
messages=[{'role': 'user', 'content': 'Explain machine learning'}],
stream=True
)
for chunk in stream:
print(chunk['message']['content'], end='', flush=True)
# Generate completion (non-chat)
response = ollama.generate(
model='llama3.2',
prompt='The capital of France is',
options={
'temperature': 0.1,
'num_predict': 50
}
)
print(response['response'])
# Get embeddings
embeddings = ollama.embeddings(
model='llama3.2',
prompt='Vector embeddings are useful for semantic search'
)
print(f"Embedding dimension: {len(embeddings['embedding'])}")OpenAI API Compatibility
from openai import OpenAI
# Point OpenAI client to Ollama
client = OpenAI(
base_url="http://localhost:11434/v1",
api_key="ollama" # Required but not used
)
# Use exactly like OpenAI API
response = client.chat.completions.create(
model="llama3.2",
messages=[
{"role": "system", "content": "You are a helpful assistant."},
{"role": "user", "content": "What is the meaning of life?"}
],
temperature=0.7,
max_tokens=500
)
print(response.choices[0].message.content)
# Streaming
stream = client.chat.completions.create(
model="llama3.2",
messages=[{"role": "user", "content": "Write a haiku about coding"}],
stream=True
)
for chunk in stream:
if chunk.choices[0].delta.content:
print(chunk.choices[0].delta.content, end="", flush=True)
# Easy switching between local and cloud
import os
def get_client():
if os.getenv("USE_LOCAL", "true").lower() == "true":
return OpenAI(base_url="http://localhost:11434/v1", api_key="ollama")
return OpenAI() # Uses OPENAI_API_KEYCreating Custom Models (Modelfile)
# Create a Modelfile for a custom assistant
cat > Modelfile << 'EOF'
FROM llama3.2
# Set the temperature for more creative responses
PARAMETER temperature 0.8
# Set context window size
PARAMETER num_ctx 4096
# System prompt
SYSTEM """
You are CodeBot, an expert programming assistant specializing in Python,
JavaScript, and cloud architecture. You provide concise, practical code
examples and explain complex concepts clearly. Always include error
handling in your code examples.
"""
# Custom template (optional)
TEMPLATE """{{ if .System }}<|start_header_id|>system<|end_header_id|>
{{ .System }}<|eot_id|>{{ end }}{{ if .Prompt }}<|start_header_id|>user<|end_header_id|>
{{ .Prompt }}<|eot_id|>{{ end }}<|start_header_id|>assistant<|end_header_id|>
{{ .Response }}<|eot_id|>"""
EOF
# Create the custom model
ollama create codebot -f Modelfile
# Run your custom model
ollama run codebot "How do I handle exceptions in Python?"
# Another example: SQL Expert
cat > SQLExpert.Modelfile << 'EOF'
FROM llama3.2
PARAMETER temperature 0.3
PARAMETER num_ctx 8192
SYSTEM """
You are a senior database administrator and SQL expert. You help users
write efficient, optimized SQL queries. Always consider:
- Query performance and indexing
- Data integrity constraints
- Security (SQL injection prevention)
- Database-specific syntax when asked
Provide explanations for complex queries.
"""
EOF
ollama create sql-expert -f SQLExpert.ModelfileBuilding a Local RAG System
import ollama
import chromadb
from chromadb.utils import embedding_functions
# Initialize ChromaDB with Ollama embeddings
class OllamaEmbeddingFunction:
def __init__(self, model: str = "llama3.2"):
self.model = model
def __call__(self, input: list[str]) -> list[list[float]]:
embeddings = []
for text in input:
response = ollama.embeddings(model=self.model, prompt=text)
embeddings.append(response['embedding'])
return embeddings
# Setup ChromaDB
client = chromadb.PersistentClient(path="./ollama_rag_db")
embedding_fn = OllamaEmbeddingFunction()
collection = client.get_or_create_collection(
name="documents",
embedding_function=embedding_fn
)
# Add documents
documents = [
"Ollama runs LLMs locally on your machine without cloud dependencies.",
"The llama.cpp backend provides efficient CPU and GPU inference.",
"Modelfiles allow you to customize model behavior and system prompts.",
"Ollama supports NVIDIA CUDA, AMD ROCm, and Apple Metal acceleration.",
"The REST API is compatible with OpenAI's chat completions format."
]
collection.add(
documents=documents,
ids=[f"doc_{i}" for i in range(len(documents))]
)
def rag_query(question: str, n_results: int = 3) -> str:
"""Answer questions using RAG with local Ollama models."""
# Retrieve relevant documents
results = collection.query(
query_texts=,
n_results=n_results
)
context = "\n".join(results['documents'][0])
# Generate answer with context
response = ollama.chat(
model='llama3.2',
messages=[
{
'role': 'system',
'content': f'Answer based on this context:\n{context}\n\nBe concise and accurate.'
},
{'role': 'user', 'content': question}
]
)
return response['message']['content']
# Example usage
answer = rag_query("How does Ollama handle GPU acceleration?")
print(answer)Model Comparison and Selection
| Model | Size | RAM Required | Best For | Speed |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| llama3.2:1b | 1.3GB | 4GB | Simple tasks, fast responses | Very Fast |
| llama3.2:3b | 2.0GB | 8GB | General purpose, balanced | Fast |
| llama3.2:70b | 40GB | 48GB+ | Complex reasoning | Slow |
| mistral:7b | 4.1GB | 8GB | General purpose, efficient | Fast |
| codellama:7b | 3.8GB | 8GB | Code generation | Fast |
| phi3:3.8b | 2.2GB | 8GB | Reasoning, math | Fast |
| gemma2:9b | 5.4GB | 12GB | General purpose | Medium |
Performance Optimization
# Check GPU availability
ollama run llama3.2 --verbose
# Environment variables for optimization
export OLLAMA_NUM_PARALLEL=4 # Concurrent requests
export OLLAMA_MAX_LOADED_MODELS=2 # Models in memory
export OLLAMA_GPU_OVERHEAD=0 # Reduce GPU memory overhead
# For NVIDIA GPUs
export CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0 # Use specific GPU
# Memory-efficient loading
ollama run llama3.2:3b-q4_0 # 4-bit quantization (smaller, faster)
ollama run llama3.2:3b-q8_0 # 8-bit quantization (better quality)
# Python: Optimize for throughput
import ollama
from concurrent.futures import ThreadPoolExecutor
def process_prompt(prompt: str) -> str:
response = ollama.generate(
model='llama3.2',
prompt=prompt,
options={
'num_ctx': 2048, # Smaller context = faster
'num_predict': 256, # Limit output length
'num_thread': 8 # CPU threads
}
)
return response['response']
# Batch processing
prompts = ["Explain AI", "What is ML?", "Define NLP"]
with ThreadPoolExecutor(max_workers=4) as executor:
results = list(executor.map(process_prompt, prompts))LangChain Integration
from langchain_ollama import OllamaLLM, OllamaEmbeddings
from langchain.prompts import ChatPromptTemplate
from langchain.chains import LLMChain
# Initialize Ollama LLM
llm = OllamaLLM(
model="llama3.2",
temperature=0.7,
num_ctx=4096
)
# Simple chain
prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages([
("system", "You are a helpful assistant that explains concepts simply."),
("human", "{question}")
])
chain = prompt | llm
response = chain.invoke({"question": "What is quantum computing?"})
print(response)
# With embeddings for RAG
embeddings = OllamaEmbeddings(model="llama3.2")
from langchain_community.vectorstores import Chroma
from langchain.text_splitter import RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter
# Create vector store with Ollama embeddings
text_splitter = RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter(chunk_size=500, chunk_overlap=50)
texts = text_splitter.split_text(long_document)
vectorstore = Chroma.from_texts(
texts,
embeddings,
persist_directory="./langchain_ollama_db"
)
# Retrieval chain
retriever = vectorstore.as_retriever(search_kwargs={"k": 3})
# ... continue with RAG chainReferences
- Ollama Official: https://ollama.com/
- Ollama GitHub: https://github.com/ollama/ollama
- Model Library: https://ollama.com/library
- Python SDK: https://github.com/ollama/ollama-python
- llama.cpp: https://github.com/ggerganov/llama.cpp
Conclusion
Ollama has made local LLM inference remarkably accessible. With automatic hardware detection, simple model management, and OpenAI API compatibility, you can build AI applications that run entirely on your hardware. Whether you're prototyping without API costs, building privacy-sensitive applications, or just exploring what's possible with open-source models, Ollama provides the foundation. Start with smaller models like Llama 3.2 1B or Phi-3 for fast iteration, then scale up to larger models as needed. The combination of Ollama with vector databases like ChromaDB enables powerful local RAG systems that rival cloud-based solutions.
Discover more from C4: Container, Code, Cloud & Context
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.